Galphas-coupled receptor signaling actively down-regulates alpha4beta1-integrin affinity: a possible mechanism for cell de-adhesion
- PMID: 18534032
- PMCID: PMC2442041
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-9-26
Galphas-coupled receptor signaling actively down-regulates alpha4beta1-integrin affinity: a possible mechanism for cell de-adhesion
Abstract
Background: Activation of integrins in response to inside-out signaling serves as a basis for leukocyte arrest on endothelium, and migration of immune cells. Integrin-dependent adhesion is controlled by the conformational state of the molecule (i.e. change in the affinity for the ligand and molecular unbending (extension)), which is regulated by seven-transmembrane Guanine nucleotide binding Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs). alpha4beta1-integrin (CD49d/CD29, Very Late Antigen-4, VLA-4) is expressed on leukocytes, hematopoietic stem cells, hematopoietic cancer cells, and others. Affinity and extension of VLA-4 are both rapidly up-regulated by inside-out signaling through several Galphai-coupled GPCRs. The goal of the current report was to study the effect of Galphas-coupled GPCRs upon integrin activation.
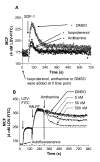
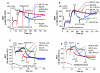
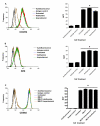
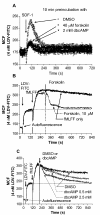
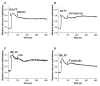
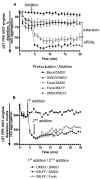
Results: Using real-time fluorescent ligand binding to assess affinity and a FRET based assay to probe alpha4beta1-integrin unbending, we show that two Galphas-coupled GPCRs (H2-histamine receptor and beta2-adrenergic receptor) as well as several cAMP agonists can rapidly down modulate the affinity of VLA-4 activated through two Galphai-coupled receptors (CXCR4 and FPR) in U937 cells and primary human peripheral blood monocytes. This down-modulation can be blocked by receptor-specific antagonists. The Galphas-induced responses were not associated with changes in the expression level of the Galphai-coupled receptors. In contrast, the molecular unbending of VLA-4 was not significantly affected by Galphas-coupled GPCR signaling. In a VLA-4/VCAM-1-specific myeloid cell adhesion system, inhibition of the VLA-4 affinity change by Galphas-coupled GPCR had a statistically significant effect upon cell aggregation.
Conclusion: We conclude that Galphas-coupled GPCRs can rapidly down modulate the affinity state of VLA-4 binding pocket through a cAMP dependent pathway. This plays an essential role in the regulation of cell adhesion. We discuss several possible implications of this described phenomenon.
Figures

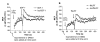
References
-
- De Meyer SF, Vanhoorelbeke K, Ulrichts H, Staelens S, Feys HB, Salles I, Fontayne A, Deckmyn H. Development of monoclonal antibodies that inhibit platelet adhesion or aggregation as potential anti-thrombotic drugs. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2006;6:191–207. doi: 10.2174/187152906778249536. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

