Beyond high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels evaluating high-density lipoprotein function as influenced by novel therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 18534265
- PMCID: PMC3315104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.016
Beyond high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels evaluating high-density lipoprotein function as influenced by novel therapeutic approaches
Abstract
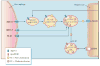
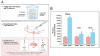
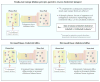
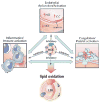
A number of therapeutic strategies targeting high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and reverse cholesterol transport are being developed to halt the progression of atherosclerosis or even induce regression. However, circulating HDL cholesterol levels alone represent an inadequate measure of therapeutic efficacy. Evaluation of the potential effects of HDL-targeted interventions on atherosclerosis requires reliable assays of HDL function and surrogate markers of efficacy. Promotion of macrophage cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport is thought to be one of the most important mechanisms by which HDL protects against atherosclerosis, and methods to assess this pathway in vivo are being developed. Indexes of monocyte chemotaxis, endothelial inflammation, oxidation, nitric oxide production, and thrombosis reveal other dimensions of HDL functionality. Robust, reproducible assays that can be performed widely are needed to move this field forward and permit effective assessment of the therapeutic potential of HDL-targeted therapies.
Figures

References
-
- Duffy D, Rader DJ. Emerging therapies targeting high-density lipoprotein metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport. Circulation. 2006;113:1140–50. - PubMed
-
- Brown BG, Zhao XQ, Chait A, et al. Simvastatin and niacin, antioxidant vitamins, or the combination for the prevention of coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1583–92. - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP, Garrison RJ, Wilson PW, Abbott RD, Kalousdian S, Kannel WB. Incidence of coronary heart disease and lipoprotein cholesterol levels. The Framingham Study. JAMA. 1986;256:2835–8. - PubMed
-
- Robins SJ, Collins D, Wittes JT, et al. Relation of gemfibrozil treatment and lipid levels with major coronary events: VA-HIT: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285:1585–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

