Area 3a neuron response to skin nociceptor afferent drive
- PMID: 18534992
- PMCID: PMC2638786
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhn086
Area 3a neuron response to skin nociceptor afferent drive
Abstract
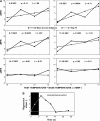
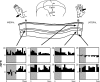
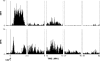
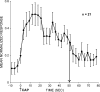
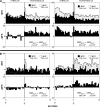
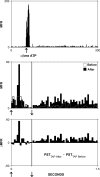
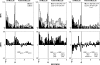
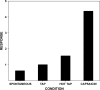
Area 3a neurons are identified that respond weakly or not at all to skin contact with a 25-38 degrees C probe, but vigorously to skin contact with the probe at > or =49 degrees C. Maximal rate of spike firing associated with 1- to 7-s contact at > or =49 degrees C occurs 1-2 s after probe removal from the skin. The activity evoked by 5-s contact with the probe at 51 degrees C remains above-background for approximately 20 s after probe retraction. After 1-s contact at 55-56 degrees C activity remains above-background for approximately 4 s. Magnitude of spike firing associated with 5-s contact increases linearly as probe temperature is increased from 49-51 degrees C. Intradermal capsaicin injection elicits a larger (approximately 2.5x) and longer-lasting (100x) increase in area 3a neuron firing rate than 5-s contact at 51 degrees C. Area 3a neurons exhibit enhanced or novel responsivity to 25-38 degrees C contact for a prolonged time after intradermal injection of capsaicin or alpha, beta methylene adenosine triphosphate. Their 1) delayed and persisting increase in spike firing in response to contact at > or =49 degrees C, 2) vigorous and prolonged response to intradermal capsaicin, and 3) enhanced and frequently novel response to 25-38 degrees C contact following intradermal algogen injection or noxious skin heating suggest that the area 3a neurons identified in this study contribute to second pain and mechanical hyperalgesia/allodynia.
Figures






References
-
- Andrew D, Craig AD. Responses of spinothalamic lamina I neurons to maintained noxious mechanical stimulation in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 2002;87:1889–1901. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Baron Y, Disbrow E, Roberts TPL. Brain processing of capsaicin-induced secondary hyperalgesia—a functional MRI study. Neurology. 1999;53:548–557. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Baron Y, Disbrow E, Roberts TPL. Activation of the somatosensory cortex during Aβ-fiber mediated hyperalgesia—a MSI study. Brain Res. 2000;871:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Baumann TK, Simone DA, Shain CN, LaMotte RH. Neurogenic hyperalgesia: The search for the primary afferent fibers that contribute to capsaicin-induced pain and hyperalgesia. J Neurophysiol. 1991;66:212–227. - PubMed

