Seizure termination by acidosis depends on ASIC1a
- PMID: 18536711
- PMCID: PMC2553357
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2132
Seizure termination by acidosis depends on ASIC1a
Abstract
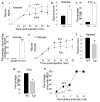
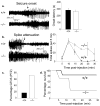
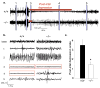
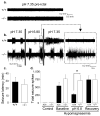
Most seizures stop spontaneously; however, the molecular mechanisms that terminate seizures remain unknown. Observations that seizures reduced brain pH and that acidosis inhibited seizures indicate that acidosis halts epileptic activity. Because acid-sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a) is exquisitely sensitive to extracellular pH and regulates neuron excitability, we hypothesized that acidosis might activate ASIC1a, which would terminate seizures. Disrupting mouse ASIC1a increased the severity of chemoconvulsant-induced seizures, whereas overexpressing ASIC1a had the opposite effect. ASIC1a did not affect seizure threshold or onset, but shortened seizure duration and prevented seizure progression. CO2 inhalation, long known to lower brain pH and inhibit seizures, required ASIC1a to interrupt tonic-clonic seizures. Acidosis activated inhibitory interneurons through ASIC1a, suggesting that ASIC1a might limit seizures by increasing inhibitory tone. Our results identify ASIC1a as an important element in seizure termination when brain pH falls and suggest both a molecular mechanism for how the brain stops seizures and new therapeutic strategies.
Figures

Comment in
-
Arresting a seizure by dropping a little Acid.Epilepsy Curr. 2009 Mar-Apr;9(2):55-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2008.01291.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2009. PMID: 19421382 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Noebels JL. The biology of epilepsy genes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:599–625. - PubMed
-
- Spencer SS, Spencer DD. Implications of seizure termination location in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1996;37:455–458. - PubMed
-
- Chapman AG, Meldrum BS, Siesjo BK. Cerebral metabolic changes during prolonged epileptic seizures in rats. J Neurochem. 1977;28:1025–1035. - PubMed
-
- Freund TF, Buzsaki G, Prohaska OJ, Leon A, Somogyi P. Simultaneous recording of local electrical activity, partial oxygen tension and temperature in the rat hippocampus with a chamber-type microelectrode. Effects of anaesthesia, ischemia and epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1989;28:539–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

