Initiation of allelic exclusion by stochastic interaction of Tcrb alleles with repressive nuclear compartments
- PMID: 18536719
- PMCID: PMC2561338
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1624
Initiation of allelic exclusion by stochastic interaction of Tcrb alleles with repressive nuclear compartments
Abstract
Studies of antigen-receptor loci have linked directed monoallelic association with pericentromeric heterochromatin to the initiation or maintenance of allelic exclusion. Here we provide evidence for a fundamentally different basis for T cell antigen receptor-beta (Tcrb) allelic exclusion. Using three-dimensional immunofluorescence in situ hybridization, we found that germline Tcrb alleles associated stochastically and at high frequency with the nuclear lamina or with pericentromeric heterochromatin in developing thymocytes and that such interactions inhibited variable-to-diversity-joining (V(beta)-to-D(beta)J(beta)) recombination before beta-selection. The introduction of an ectopic enhancer into Tcrb resulted in fewer such interactions and impaired allelic exclusion. We propose that initial V(beta)-to-D(beta)J(beta) recombination events are generally monoallelic in developing thymocytes because of frequent stochastic, rather than directed, interactions of Tcrb alleles with repressive nuclear compartments. Such interactions may be essential for Tcrb allelic exclusion.
Figures


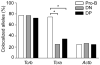
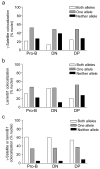
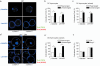

Comment in
-
Nuclear geography and allelic exclusion.Nat Immunol. 2008 Jul;9(7):718-20. doi: 10.1038/ni0708-718. Nat Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18563080 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bassing CH, Swat W, Alt FW. The mechanism and regulation of chromosomal V(D)J recombination. Cell. 2002;109(Suppl):S45–55. - PubMed
-
- Michie AM, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Regulation of thymocyte differentiation: pre-TCR signals and β-selection. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Khor B, Sleckman BP. Allelic exclusion at the TCRβ locus. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:230–234. - PubMed
-
- Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, Rajewsky K. The lingering enigma of the allelic exclusion mechanism. Cell. 2004;118:539–544. - PubMed
-
- Jackson AM, Krangel MS. Turning T-cell receptor β recombination on and off: more questions than answers. Immunol Rev. 2006;209:129–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

