Bimodal effects of the Kv7 channel activator retigabine on vascular K+ currents
- PMID: 18536747
- PMCID: PMC2527845
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.231
Bimodal effects of the Kv7 channel activator retigabine on vascular K+ currents
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study investigated the functional and electrophysiological effects of the Kv7 channel activator, retigabine, on murine portal vein smooth muscle.
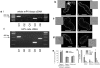
Experimental approach: KCNQ gene expression was determined by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunocytochemical experiments. Whole cell voltage clamp and current clamp were performed on isolated myocytes from murine portal vein. Isometric tension recordings were performed on whole portal veins. K+ currents generated by KCNQ4 and KCNQ5 expression were recorded by two-electrode voltage clamp in Xenopus oocytes.
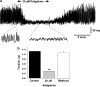
Key results: KCNQ1, 4 and 5 were expressed in mRNA derived from murine portal vein, either as whole tissue or isolated myocytes. Kv7.1 and Kv7.4 proteins were identified in the cell membranes of myocytes by immunocytochemistry. Retigabine (2-20 microM) suppressed spontaneous contractions in whole portal veins, hyperpolarized the membrane potential and augmented potassium currents at -20 mV. At more depolarized potentials, retigabine and flupirtine, decreased potassium currents. Both effects of retigabine were prevented by prior application of the K(v)7 blocker XE991 (10 muM). Recombinant KCNQ 4 or 5 channels were only activated by retigabine or flupirtine.
Conclusions and implications: The Kv7 channel activators retigabine and flupirtine have bimodal effects on vascular potassium currents, which are not seen with recombinant KCNQ channels. These results provide support for KCNQ4- or KCNQ5-encoded channels having an important functional impact in the vasculature.
Figures
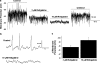





References
-
- Dupuis DS, Olesen S-P, Jespersen T, Christensen JK, Christophersen P, Jensen BS. Activation of KCNQ5 Channels stably expressed in HEK293 cells by BMS-204352. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;437:129–137. - PubMed
-
- Jentsch TJ. Neuronal KCNQ potassium channels: physiology and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:21–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

