Contribution of amino acid region 334-335 from factor Va heavy chain to the catalytic efficiency of prothrombinase
- PMID: 18537263
- PMCID: PMC2652359
- DOI: 10.1021/bi800057r
Contribution of amino acid region 334-335 from factor Va heavy chain to the catalytic efficiency of prothrombinase
Abstract
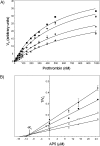
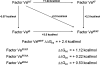
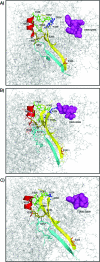
We have demonstrated that amino acids E (323), Y (324), E (330), and V (331) from the factor Va heavy chain are required for the interaction of the cofactor with factor Xa and optimum rates of prothrombin cleavage. We have also shown that amino acid region 332-336 contains residues that are important for cofactor function. Using overlapping peptides, we identified amino acids D (334) and Y (335) as contributors to cofactor activity. We constructed recombinant factor V molecules with the mutations D (334) --> K and Y (335) --> F (factor V (KF)) and D (334) --> A and Y (335) --> A (factor V (AA)). Kinetic studies showed that while factor Va (KF) and factor Va (AA) had a K D for factor Xa similar to the K D observed for wild-type factor Va (factor Va (WT)), the clotting activities of the mutant molecules were impaired and the k cat of prothrombinase assembled with factor Va (KF) and factor Va (AA) was reduced. The second-order rate constant of prothrombinase assembled with factor Va (KF) or factor Va (AA) for prothrombin activation was approximately 10-fold lower than the second-order rate constant for the same reaction catalyzed by prothrombinase assembled with factor Va (WT). We also created quadruple mutants combining mutations in the amino acid region 334-335 with mutations at the previously identified amino acids that are important for factor Xa binding (i.e., E (323)Y (324) and E (330)V (331)). Prothrombinase assembled with the quadruple mutant molecules displayed a second-order rate constant up to 400-fold lower than the values obtained with prothrombinase assembled with factor Va (WT). The data demonstrate that amino acid region 334-335 is required for the rearrangement of enzyme and substrate necessary for efficient catalysis of prothrombin by prothrombinase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cooperative regulation of the activity of factor Xa within prothrombinase by discrete amino acid regions from factor Va heavy chain.Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 2;47(48):12835-43. doi: 10.1021/bi801241r. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18991406 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of amino acid region 659-663 of Factor Va heavy chain to the activity of factor Xa within prothrombinase.Biochemistry. 2010 Oct 5;49(39):8520-34. doi: 10.1021/bi101097t. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20722419 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the acidic hirudin-like COOH-terminal amino acid region of factor Va heavy chain in the enhanced function of prothrombinase.Biochemistry. 2008 Jul 29;47(30):7963-74. doi: 10.1021/bi800593k. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18590276 Free PMC article.
-
Blood coagulation factor Va's key interactive residues and regions for prothrombinase assembly and prothrombin binding.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;17(8):1229-1239. doi: 10.1111/jth.14487. Epub 2019 Jun 17. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31102425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coagulation factor V: a plethora of anticoagulant molecules.Curr Opin Hematol. 2005 Mar;12(2):141-8. doi: 10.1097/01.moh.0000155016.30296.90. Curr Opin Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15725905 Review.
Cited by
-
The Dual Regulatory Role of Amino Acids Leu480 and Gln481 of Prothrombin.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jan 22;291(4):1565-1581. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.691956. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26601957 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative regulation of the activity of factor Xa within prothrombinase by discrete amino acid regions from factor Va heavy chain.Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 2;47(48):12835-43. doi: 10.1021/bi801241r. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18991406 Free PMC article.
-
Amino acid region 1000-1008 of factor V is a dynamic regulator for the emergence of procoagulant activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 27;288(52):37026-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462374. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24178294 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the prothrombin-binding site of pseutarin C by site-directed PEGylation.Blood. 2022 May 12;139(19):2972-2982. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014878. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35148539 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of amino acid region 659-663 of Factor Va heavy chain to the activity of factor Xa within prothrombinase.Biochemistry. 2010 Oct 5;49(39):8520-34. doi: 10.1021/bi101097t. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20722419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalafatis M.; Egan J. O.; van’t Veer C.; Cawthern K. M.; Mann K. G. (1997) The regulation of clotting factors. Crit. Rev. Eukaryotic Gene Expression 7, 241–280. - PubMed
-
- Kalafatis M.; Mann K. G. (2001) Factor V: Dr. Jeckyll and Mr. Hyde. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 489, 31–43. - PubMed
-
- Rosing J.; Zwaal R. F.; Tans G. (1986) Formation of meizothrombin as intermediate in factor Xa-catalyzed prothrombin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 4224–4228. - PubMed
-
- Owen W. G.; Esmon C. T.; Jackson C. M. (1974) The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. I. Characterization of the reaction products formed during the activation of bovine prothrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 594–605. - PubMed
-
- Esmon C. T.; Owen W. G.; Jackson C. M. (1974) The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. II. Differentiation between thrombin- and factor Xa-catalyzed proteolyses. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 606–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

