Molecular characterization of CYP2B6 substrates
- PMID: 18537573
- PMCID: PMC2426921
- DOI: 10.2174/138920008784746346
Molecular characterization of CYP2B6 substrates
Abstract
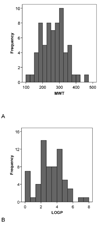
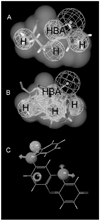
CYP2B6 has not been as fully characterized at the molecular level as other members of the human cytochrome P450 family. As more widely used in vitro probes for characterizing the involvement of this enzyme in the metabolism of xenobiotics have become available, the number of molecules identified as CYP2B6 substrates has increased. In this study we have analyzed the available kinetic data generated by multiple laboratories with human recombinant expressed CYP2B6 and along with calculated molecular properties derived from the ChemSpider database, we have determined the molecular features that appear to be important for CYP2B6 substrates. In addition we have applied 2D and 3D QSAR methods to generate predictive pharmacophore and 2D models. For 28 molecules with K(m) data, the molecular weight (mean +/- SD) is 253.78+/-74.03, ACD/logP is 2.68+/-1.51, LogD(pH 5.5) is 1.51+/-1.43, LogD(pH 7.4) is 2.02+/-1.25, hydrogen bond donor (HBD) count is 0.57 +/-0.57, hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) count is 2.57+/-1.37, rotatable bonds is 3.50+/-2.71 and total polar surface area (TPSA) is 27.63+/-19.42. A second set of 15 molecules without K(m) data possessed similar mean molecular property values. These properties are comparable to those of a set of 21 molecules used in a previous pharmacophore modeling study (Ekins et al., J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288 (1), 21-29, 1999). Only the LogD and HBD values were statistically significantly different between these different datasets. We have shown that CYP2B6 substrates are generally small hydrophobic molecules that are frequently central nervous system active, which may be important for drug discovery research.
Figures




References
-
- Kumagai J, Fujimura T, Takahashi S, Urano T, Ogushi T, Horie-Inoue K, Ouchi Y, Kitamura T, Muramatsu M, Blumberg B, Inoue S. Prostate. 2007;67:1029–1037. - PubMed
-
- Ekins S, VandenBranden M, Ring BJ, Wrighton SA. Pharmacogenetics. 1997;7:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Ekins S, Vandenbranden M, Ring BJ, Gillespie JS, Yang TJ, Gelboin HV, Wrighton SA. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;286:1253–1259. - PubMed
-
- Ekins S, Wrighton SA. Drug Metab Rev. 1999;31:719–754. - PubMed
-
- Ekins S, Bravi G, Ring BJ, Gillespie TA, Gillespie JS, Vandenbranden M, Wrighton SA, Wikel JH. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 288:21–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

