A simple and accurate SNP scoring strategy based on typeIIS restriction endonuclease cleavage and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
- PMID: 18538037
- PMCID: PMC2442615
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-276
A simple and accurate SNP scoring strategy based on typeIIS restriction endonuclease cleavage and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
Abstract
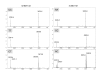
Background: We describe the development of a novel matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF)-based single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) scoring strategy, termed Restriction Fragment Mass Polymorphism (RFMP) that is suitable for genotyping variations in a simple, accurate, and high-throughput manner. The assay is based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and mass measurement of oligonucleotides containing a polymorphic base, to which a typeIIS restriction endonuclease recognition was introduced by PCR amplification. Enzymatic cleavage of the products leads to excision of oligonucleotide fragments representing base variation of the polymorphic site whose masses were determined by MALDI-TOF MS.
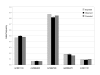
Results: The assay represents an improvement over previous methods because it relies on the direct mass determination of PCR products rather than on an indirect analysis, where a base-extended or fluorescent report tag is interpreted. The RFMP strategy is simple and straightforward, requiring one restriction digestion reaction following target amplification in a single vessel. With this technology, genotypes are generated with a high call rate (99.6%) and high accuracy (99.8%) as determined by independent sequencing.
Conclusion: The simplicity, accuracy and amenability to high-throughput screening analysis should make the RFMP assay suitable for large-scale genotype association study as well as clinical genotyping in laboratories.
Figures

References
-
- Faruqi AF, Hosono S, Driscoll MD, Dean FB, Alsmadi O, Bandaru R, Kumar G, Grimwade B, Zong Q, Sun Z, Du Y, Kingsmore S, Knott T, Lasken RS. High-throughput genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms with rolling circle amplification. BMC Genomics. 2001;2:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-2-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hall JG, Eis PS, Law SM, Reynaldo LP, Prudent JR, Marshall DJ, Allawi HT, Mast AL, Dahlberg JE, Kwiatkowski RW, de Arruda M, Neri BP, Lyamichev VI. Sensitive detection of DNA polymorphisms by the serial invasive signal amplification reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:8272–8277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140225597. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buetow KH, Edmonson M, MacDonald R, Clifford R, Yip P, Kelley J, Little DP, Strausberg R, Koester H, Cantor CR, Braun A. High-throughput development and characterization of a genomewide collection of gene-based single nucleotide polymorphism markers by chip-based matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:581–584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.021506298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

