Distinct eRF3 requirements suggest alternate eRF1 conformations mediate peptide release during eukaryotic translation termination
- PMID: 18538658
- PMCID: PMC2475577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.020
Distinct eRF3 requirements suggest alternate eRF1 conformations mediate peptide release during eukaryotic translation termination
Abstract
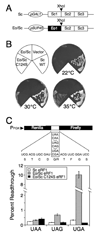
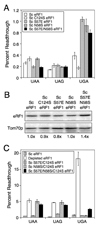
Organisms that use the standard genetic code recognize UAA, UAG, and UGA as stop codons, whereas variant code species frequently alter this pattern of stop codon recognition. We previously demonstrated that a hybrid eRF1 carrying the Euplotes octocarinatus domain 1 fused to Saccharomyces cerevisiae domains 2 and 3 (Eo/Sc eRF1) recognized UAA and UAG, but not UGA, as stop codons. In the current study, we identified mutations in Eo/Sc eRF1 that restore UGA recognition and define distinct roles for the TASNIKS and YxCxxxF motifs in eRF1 function. Mutations in or near the YxCxxxF motif support the cavity model for stop codon recognition by eRF1. Mutations in the TASNIKS motif eliminated the eRF3 requirement for peptide release at UAA and UAG codons, but not UGA codons. These results suggest that the TASNIKS motif and eRF3 function together to trigger eRF1 conformational changes that couple stop codon recognition and peptide release during eukaryotic translation termination.
Figures




References
-
- Alkalaeva EZ, Pisarev AV, Frolova LY, Kisselev LL, Pestova TV. In Vitro Reconstitution of Eukaryotic Translation Reveals Cooperativity between Release Factors eRF1 and eRF3. Cell. 2006;125:1125–1136. - PubMed
-
- Bonetti B, Fu L, Moon J, Bedwell DM. The efficiency of translation termination is determined by a synergistic interplay between upstream and downstream sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1995;251:334–345. - PubMed
-
- Eurwilaichitr L, Graves FM, Stansfield I, Tuite MF. The C-terminus of eRF1 defines a functionally important domain for translation termination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol. 1999;32:485–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

