Region-specific involvement of AMPA/Kainate receptors in Fos protein expression induced by cocaine-conditioned cues
- PMID: 18539009
- PMCID: PMC4798851
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2008.04.010
Region-specific involvement of AMPA/Kainate receptors in Fos protein expression induced by cocaine-conditioned cues
Abstract
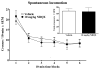
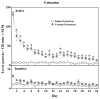
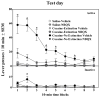
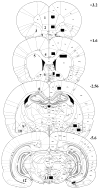
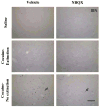
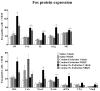
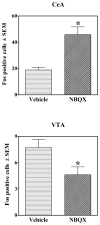
This study investigated the effects of the AMPA/Kainate receptor antagonist, NBQX, on cue-elicited cocaine-seeking behavior and concomitant changes in Fos protein expression. After cocaine self-administration training, rats underwent 24 days of abstinence during which they were exposed daily either to the self-administration environment with response-contingent cues previously paired with cocaine infusions available (Extinction group) or to an alternate environment (No Extinction group). Subsequently, rats were tested for cocaine-seeking behavior (i.e., operant responses without cocaine reinforcement) elicited by the cocaine-associated cues after pretreatment with either vehicle or NBQX (10 mg/kg, IP). NBQX markedly attenuated cue-elicited cocaine-seeking behavior relative to vehicle pretreatment in the No Extinction group and also decreased cue-elicited Fos protein expression in a region-specific manner in the anterior cingulate and orbitofrontal cortices, basolateral amygdala, nucleus accumbens core, and dorsal caudate-putamen, suggesting involvement of AMPA glutamate systems in specific subregions of the neuronal circuitry activated by cocaine cues.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Environmental living conditions introduced during forced abstinence alter cocaine-seeking behavior and Fos protein expression.Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 29;171(4):1187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20933585 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007 Jul;192(4):571-80. doi: 10.1007/s00213-007-0753-8. Epub 2007 Mar 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17347848
-
c-Fos expression associated with reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior by response-contingent conditioned cues.Synapse. 2009 Oct;63(10):823-35. doi: 10.1002/syn.20666. Synapse. 2009. PMID: 19533625 Free PMC article.
-
Fos activation of selective afferents to ventral tegmental area during cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13309-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2277-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993446 Free PMC article.
-
Do AMPA/kainate antagonists possess potential in the treatment of addiction? Evidence from animal behavioural studies.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 2;138:111355. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2025.111355. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40187601 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent social isolation increases cocaine seeking in male and female mice.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Feb 1;359:589-596. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.10.007. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30296530 Free PMC article.
-
Factors regulating serine racemase and d-amino acid oxidase expression in the mouse striatum.Brain Res. 2021 Jan 15;1751:147202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147202. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33171153 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortical regulation of drug seeking in animal models of drug relapse.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010;3:101-17. doi: 10.1007/7854_2009_19. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21161751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental living conditions introduced during forced abstinence alter cocaine-seeking behavior and Fos protein expression.Neuroscience. 2010 Dec 29;171(4):1187-96. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20933585 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the rostral basolateral amygdala and prelimbic prefrontal cortex in regulating reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010 Sep;96(3):347-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2010.06.005. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2010. PMID: 20600250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta JI, Thiel KJ, Sanabria F, Browning JR, Neisewander JL. Effect of schedule or reinforcement on cue reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Behavioural Pharmacology. 2008;19:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Alleweireldt AT, Hobbs RJ, Taylor AR, Neisewander JL. Effects of SCH-23390 infused into the amygdala or adjacent cortex and basal ganglia on cocaine seeking and self-administration in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31:363–374. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom P, Hyytia P. Attenuation of cocaine-seeking behaviour by the AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist CNQX in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;166:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom P, Hyytia P. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonism attenuates cue-induced cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacolog. 2006;31:778–786. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom P, Hyytia P. Involvement of AMPA/kainate, NMDA, and mGlu5 receptors in the nucleus accumbens core in cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2007;192:571–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

