Antigen-specific T-T interactions regulate CD4 T-cell expansion
- PMID: 18539897
- PMCID: PMC2515122
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-114389
Antigen-specific T-T interactions regulate CD4 T-cell expansion
Abstract
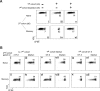
The regulation of CD4 T-cell numbers during an immune response should take account of the amount of antigen (Ag), the initial frequency of Ag-specific T cells, the mix of naive versus experienced cells, and (ideally) the diversity of the repertoire. Here we describe a novel mechanism of T-cell regulation that potentially deals with all of these parameters. We found that CD4 T cells establish a negative feedback loop by capturing their cognate major histocompatibility class (MHC)/peptide complexes from Ag-presenting cells and presenting them to Ag-experienced CD4 T cells, thereby inhibiting their recruitment into the response while allowing recruitment of naive T cells. The inhibition is Ag specific, begins at day 2 (long before Ag disappearance), and cannot be overcome by providing new Ag-loaded dendritic cells. In this way, CD4 T-cell proliferation is regulated in a functional relationship to the amount of Ag, while allowing naive T cells to generate repertoire variety.
Figures




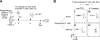
References
-
- Dutton RW, Bradley LM, Swain SL. T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:201–223. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Sprent J, Surh CD. T cell memory. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:551–579. - PubMed
-
- Merica R, Khoruts A, Pape KA, Reinhardt RL, Jenkins MK. Antigen-experienced CD4 T cells display a reduced capacity for clonal expansion in vivo that is imposed by factors present in the immune host. J Immunol. 2000;164:4551–4557. - PubMed
-
- Badovinac VP, Porter BB, Harty JT. CD8+ T cell contraction is controlled by early inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:809–817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

