18O kinetic isotope effects in non-heme iron enzymes: probing the nature of Fe/O2 intermediates
- PMID: 18540575
- PMCID: PMC2788235
- DOI: 10.1021/ja800265s
18O kinetic isotope effects in non-heme iron enzymes: probing the nature of Fe/O2 intermediates
Abstract
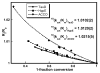
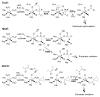
Contrasted here are the competitive 18O/16O kinetic isotope effects (18O KIEs) on kcat/Km(O2) for three non-heme iron enzymes that activate O2 at an iron center coordinated by a 2-His-1-carboxylate facial triad: taurine dioxygenase (TauD), (S)-(2)-hydroxypropylphosphonic acid epoxidase (HppE), and 1-aminocyclopropyl-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACCO). Measured 18O KIEs of 1.0102 +/- 0.0002 (TauD), 1.0120 +/- 0.0002 (HppE), and 1.0215 +/- 0.0005 (ACCO) suggest the formation in the rate-limiting step of O2 activation of an FeIII-peroxohemiketal, FeIII-OOH, and FeIV O species, respectively. The comparison of the measured 18O KIEs with calculated or experimental 18O equilibrium isotope effects (18O EIEs) provides new insights into the O2 activation through an inner-sphere mechanism at a non-heme iron center.
Figures
References
-
- Costas M, Mehn MP, Jensen MP, Que L., Jr Chem Rev. 2004;104:939. - PubMed
-
- Roth JP, Klinman JP. In: Isotopes Effects in Chemistry and Biology. Limbach H-H, editor. Marcel Dekker; New York: 2004. p. 645.
-
- Roth JP. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007;11:142. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorn E, vanderPloeg JR, Kertesz MA, Leisinger T. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:23031. - PubMed
-
- Price JC, Barr EW, Tirupati B, Bollinger JM, Krebs C. Biochemistry. 2003;42:7497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

