FTY720 rescue therapy in the dark agouti rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: expression of central nervous system genes and reversal of blood-brain-barrier damage
- PMID: 18540945
- PMCID: PMC8094834
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00182.x
FTY720 rescue therapy in the dark agouti rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: expression of central nervous system genes and reversal of blood-brain-barrier damage
Abstract
FTY720 (fingolimod) is an oral sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator in phase III development for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. To further investigate its mode of action, we analyzed gene expression in the central nervous system (CNS) during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). FTY720 downregulated inflammatory genes in addition to vascular adhesion molecules. It decreased the matrix metalloproteinase gene MMP-9 and increased its counterregulator--tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase, TIMP-1--resulting in a proteolytic balance that favors preservation of blood-brain-barrier (BBB) integrity. Furthermore, FTY720 reduced S1P lyase that increases the S1P concentration in the brain, in line with a marked reversal of neurological deficits and raising the possibility for enhanced triggering of S1P receptors on resident brain cells. This is accompanied by an increase in S1P(1) and S1P(5) in contrast with the attenuation of S1P(3) and S1P(4). Late-stage rescue therapy with FTY720, even up to 1 month after EAE onset, reversed BBB leakiness and reduced demyelination, along with normalization of neurologic function. Our results indicate rapid blockade of ongoing disease processes by FTY720, and structural restoration of the CNS parenchyma, which is likely caused by the inhibition of autoimmune T cell infiltration and direct modulation of microvascular and/or glial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


 ) and FTY70 (▪) on days 11 and 29. Panels C and D demonstrate differences between the two groups that are >10‐fold at one or both time points. Expression levels with <fivefold differences (Appendix 2), even if significant for one or both days, are not shown. Level of significance between the vehicle and FTY720 groups was determined by a student t‐test for each gene. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: PCR = polymerase chain reaction; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; DA = Dark Agouti; FTY720 = fingolimod; SEM = standard error of mean.
) and FTY70 (▪) on days 11 and 29. Panels C and D demonstrate differences between the two groups that are >10‐fold at one or both time points. Expression levels with <fivefold differences (Appendix 2), even if significant for one or both days, are not shown. Level of significance between the vehicle and FTY720 groups was determined by a student t‐test for each gene. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: PCR = polymerase chain reaction; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; DA = Dark Agouti; FTY720 = fingolimod; SEM = standard error of mean.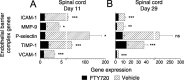
 ) versus FTY70 (▪) groups are indicated, as determined by student t‐test. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: PCR = polymerase chain reaction; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; DA = Dark Agouti; FTY720 = fingolimod; SEM = standard error of mean; ns = not significant.
) versus FTY70 (▪) groups are indicated, as determined by student t‐test. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: PCR = polymerase chain reaction; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; DA = Dark Agouti; FTY720 = fingolimod; SEM = standard error of mean; ns = not significant.

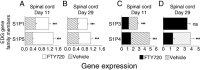
 ; n = 6) and significantly increased by FTY720 0.3 mg/kg treatment (□; n = 6). (C–D) The reciprocal situation occurs for S1P3 and S1P4 expression in the spinal cord, as these receptors are upregulated in the vehicle controls (
; n = 6) and significantly increased by FTY720 0.3 mg/kg treatment (□; n = 6). (C–D) The reciprocal situation occurs for S1P3 and S1P4 expression in the spinal cord, as these receptors are upregulated in the vehicle controls ( ; n = 6) and reduced by FTY720 treatment (▪; n = 6); an exception is no difference in S1P3 on day 29. Spinal cord expression ± SEM of the S1P receptors in naïve animals (n = 6 rats) ranged from 1.16 ± 0.05 (S1P1), 1.07 ± 0.06 (S1P3), 0.60 ± 0.051 (S1P4) to 1.20 ± 0.06 (S1P5). ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: FTY720 = fingolimod; DA = Dark Agouti; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; S1P = sphingosine‐1 phosphate; SEM = standard error of mean; ns = not significant.
; n = 6) and reduced by FTY720 treatment (▪; n = 6); an exception is no difference in S1P3 on day 29. Spinal cord expression ± SEM of the S1P receptors in naïve animals (n = 6 rats) ranged from 1.16 ± 0.05 (S1P1), 1.07 ± 0.06 (S1P3), 0.60 ± 0.051 (S1P4) to 1.20 ± 0.06 (S1P5). ***P ≤ 0.001. Abbreviations: FTY720 = fingolimod; DA = Dark Agouti; EAE = experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; S1P = sphingosine‐1 phosphate; SEM = standard error of mean; ns = not significant.
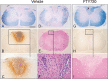
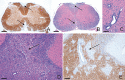
References
-
- Balatoni B, Storch MK, Swoboda EM, Schönborn V, Koziel A, Lambrou GN et al (2007) FTY720 sustains and restores neuronal function in MOG‐induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res Bull 74:307–316. - PubMed
-
- Bandhuvula P, Tam YY, Oskouian B, Saba JD (2005) The immune modulator FTY720 inhibits sphingosine‐1‐phosphate lyase activity. J Biol Chem 280:33697–33700. - PubMed
-
- Barral DC, Brenner MB (2007) CD1 antigen presentation: how it works. Nat Rev Immunol 7:929–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

