Multiple sclerosis risk after optic neuritis: final optic neuritis treatment trial follow-up
- PMID: 18541792
- PMCID: PMC2440583
- DOI: 10.1001/archneur.65.6.727
Multiple sclerosis risk after optic neuritis: final optic neuritis treatment trial follow-up
Abstract
Objective: To assess the risk of developing multiple sclerosis (MS) after optic neuritis and the factors predictive of high and low risk.
Design: Subjects in the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial, who were enrolled between July 1, 1988, and June 30, 1991, were followed up prospectively for 15 years, with the final examination in 2006.
Setting: Neurologic and ophthalmologic examinations at 13 clinical sites.
Participants: Three hundred eighty-nine subjects with acute optic neuritis.
Main outcome measures: Development of MS and neurologic disability assessment.
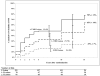
Results: The cumulative probability of developing MS by 15 years after onset of optic neuritis was 50% (95% confidence interval, 44%-56%) and strongly related to presence of lesions on a baseline non-contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain. Twenty-five percent of patients with no lesions on baseline brain MRI developed MS during follow-up compared with 72% of patients with 1 or more lesions. After 10 years, the risk of developing MS was very low for patients without baseline lesions but remained substantial for those with lesions. Among patients without lesions on MRI, baseline factors associated with a substantially lower risk for MS included male sex, optic disc swelling, and certain atypical features of optic neuritis.
Conclusions: The presence of brain MRI abnormalities at the time of an optic neuritis attack is a strong predictor of the 15-year risk of MS. In the absence of MRI-detected lesions, male sex, optic disc swelling, and atypical clinical features of optic neuritis are associated with a low likelihood of developing MS. This natural history information is important when considering prophylactic treatment for MS at the time of a first acute onset of optic neuritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Optic neuritis and the risk of multiple sclerosis--what can we learn from a brain MRI scan?Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008 Oct;4(10):532-3. doi: 10.1038/ncpneuro0911. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18779851 No abstract available.
-
Neuromyelitis optica and the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial.Arch Neurol. 2008 Nov;65(11):1545-6; author reply 1546. doi: 10.1001/archneur.65.11.1545-c. Arch Neurol. 2008. PMID: 19001178 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ebers GC. Optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1985;42:702–704. - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Arrington J, Murtagh FR, Cleary PA, Kaufman DI Optic Neuritis Study Group. Brain magnetic resonance imaging in acute optic neuritis: experience of the Optic Neuritis Study Group. Arch Neurol. 1993;50:841–846. - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Cleary PA, Anderson MM, Jr, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of corticosteroids in the treatment of acute optic neuritis. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:581–588. - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Cleary PA The Optic Neuritis Study Group. Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial: One-year follow-up results. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:773–775. - PubMed
-
- Beck RW, Cleary PA, Trobe JD, et al. The effect of corticosteroids for acute optic neuritis on the subsequent development of multiple sclerosis. N Eng J Med. 1993;329:1764–1769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

