PDK-1 regulates lactate production in hypoxia and is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cancer
- PMID: 18542064
- PMCID: PMC2441961
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604356
PDK-1 regulates lactate production in hypoxia and is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous cancer
Abstract
Here we describe the expression and function of a HIF-1-regulated protein pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-1 (PDK-1) in head and neck squamous cancer (HNSCC). Using RNAi to downregulate hypoxia-inducible PDK-1, we found that lactate and pyruvate excretion after 16-48 h of hypoxia was suppressed to normoxic levels. This indicates that PDK-1 plays an important role in maintaining glycolysis. Knockdown had no effect on proliferation or survival under hypoxia. The immunohistochemical expression of PDK-1 was assessed in 140 cases of HNSCC. PDK-1 expression was not expressed in normal tissues but was upregulated in HNSCC and found to be predominantly cytoplasmic with occasional strong focal nuclear expression. It was strongly related to poor outcome (P=0.005 split by median). These results indicate that HIF regulation of PDK-1 has a key role in maintaining lactate production in human cancer and that the investigation of PDK-1 inhibitors should be investigated for antitumour effects.
Figures
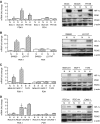
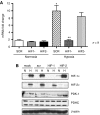
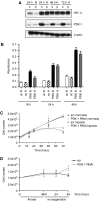

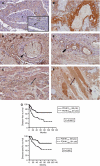
References
-
- Berridge MV, Tan AS (1993) Characterization of the cellular reduction of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT): subcellular localization, substrate dependence, and involvement of mitochondrial electron transport in MTT reduction. Arch Biochem Biophys 303: 474–482 - PubMed
-
- Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouysségur J (2007) Hypoxia signalling controls metabolic demand. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19: 1–7 - PubMed
-
- Brizel DM, Schroeder T, Scher RL, Walenta S, Clough RW, Dewhirst MW, Mueller-Klieser W (2001) Elevated tumor lactate concentrations predict for an increased risk of metastases in head-and-neck cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51: 349–353 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

