Pemetrexed plus carboplatin in elderly patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: combined analysis of two phase II trials
- PMID: 18542071
- PMCID: PMC2453025
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604442
Pemetrexed plus carboplatin in elderly patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: combined analysis of two phase II trials
Abstract
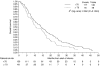
The incidence of malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) in elderly patients is increasing. In this study, pooled data from two phase II trials of pemetrexed and carboplatin (PC) as first-line therapy were retrospectively analysed for comparisons between age groups. Patients received pemetrexed 500 mg m(-2) and carboplatin AUC 5 mg ml(-1) min(-1) intravenously every 21 days with standard vitamin supplementation. Elderly patients were defined as those >or=70 years old. A total of 178 patients with an ECOG performance status of <or=2 were included. Median age was 65 years (range 38-79), with 48 patients >or=70 years (27%). Grade 3-4 haematological toxicity was slightly worse in >or=70 vs <70-year-old patients, with neutropenia observed in 25.0 vs 13.8% (P=0.11), anaemia in 20.8 vs 6.9% (P=0.01) and thrombocytopenia in 14.6 vs 8.5% (P=0.26). Non-haematological toxicity was mild and similar in the two groups. No significant difference was observed in terms of overall disease control (60.4 vs 66.9%, P=0.47), time to progression (7.2 vs 7.5 months, P=0.42) and survival (10.7 vs 13.9 months, P=0.12). Apart from slightly worse haematological toxicity, there was no significant difference in outcome or toxicity between age groups. The PC regimen is effective and well tolerated in selected elderly patients with MPM.
Figures


References
-
- Agresti A (1992) A survey of exact inference for contingency tables. Stat Sci 7: 131–177
-
- Byrne MJ, Nowak AK (2004) Modified RECIST criteria for assessment of response in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann Oncol 15: 257–260 - PubMed
-
- Castagneto B, Botta M, Aitini E, Spigno F, Degiovanni D, Alabiso O, Serra M, Muzio A, Carbone R, Buosi R, Galbusera V, Piccolini E, Giaretto L, Rebella L, Mencoboni M (2008) Phase II study of pemetrexed in combination with carboplatin in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). Ann Oncol 19: 370–373 - PubMed
-
- Ceresoli GL, Chiti A, Zucali PA, Cappuzzo F, De Vincenzo F, Cavina R, Rodari M, Poretti D, Lutman FR, Santoro A (2007a) Assessment of tumor response in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Treat Rev 33: 533–541 - PubMed
-
- Ceresoli GL, Gridelli C, Santoro A (2007b) Multidisciplinary treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncologist 12: 850–863 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

