Tetracycline to prevent epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced skin rashes: results of a placebo-controlled trial from the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (N03CB)
- PMID: 18543329
- PMCID: PMC3918166
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.23621
Tetracycline to prevent epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced skin rashes: results of a placebo-controlled trial from the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (N03CB)
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors are effective cancer therapies, but they are reported to cause a rash in >50% of patients. In the current study, the authors examined the use of tetracycline for rash prevention.
Methods: This placebo-controlled, double-blinded trial enrolled patients who were starting cancer treatment with an EGFR inhibitor. Patients could not have had a rash at the time of enrollment. All patients were randomly assigned to receive either tetracycline at a dose of 500 mg orally twice a day for 28 days versus a placebo. Patients were monitored for rash (through monthly physician assessment and weekly patient-reported questionnaires), quality of life (using the SKINDEX-16, a skin-specific quality of life index), and adverse events. Monitoring occurred during the 4-week intervention and then for an additional 4 weeks. The primary objective of the current study was to compare the incidence of rash between the study arms, and the enrollment of 30 patients per arm provided a 90% probability of detecting a 40% difference in incidence with a P value of .05 (2-sided).
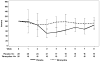
Results: A total of 61 evaluable patients were enrolled. The 2 treatment arms were well balanced with regard to baseline characteristics, dropout rates, and rates of discontinuation of the EGFR inhibitor. The incidence of rash was found to be comparable across treatment arms. Physicians reported that 16 patients treated with tetracycline (70%) and 22 patients treated with placebo (76%) developed a rash (P = .61). Tetracycline appears to have lessened the rash severity, although the high dropout rates invite caution when interpreting these findings. By Week 4, physician-reported grade 2 rash (using the National Cancer Institute's Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events [version 3.0]) occurred in 17% of tetracycline-treated patients (n = 4 patients) and in 55% of placebo-exposed patients (n = 16 patients) (P = .04). Patients treated with tetracycline reported better scores, as per the SKINDEX-16, on certain quality-of-life parameters such as skin burning or stinging, skin irritation, and being bothered by the persistence/recurrence of a skin condition. Adverse events were found to be comparable across treatment arms.
Conclusions: In the current study, tetracycline was not found to prevent EGFR inhibitor-induced rashes and therefore cannot be clinically recommended for this purpose. However, preliminary observations of diminished rash severity and improved quality of life suggest this antibiotic merits further study.
2008 American Cancer Society
Figures
References
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodriques Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJ, et al. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1201–1208. - PubMed
-
- Hochster HS, Haller DG, de Gramont A, et al. Consensus report of the international society of gastrointestinal oncology on therapeutic progress in advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 2006;107:676–685. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:567–578. - PubMed
-
- Patiyil S, Chan SN, Jatoi A. New agents, new rashes: an update on skin complications from cancer chemotherapy. Curr Oncol Rep. 2006;8:269–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10 CA035267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 CA131099/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035269/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-37404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35103/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35267/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63849/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

