Remotely triggered liposome release by near-infrared light absorption via hollow gold nanoshells
- PMID: 18543914
- PMCID: PMC2593911
- DOI: 10.1021/ja802656d
Remotely triggered liposome release by near-infrared light absorption via hollow gold nanoshells
Abstract
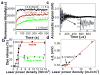
An elusive goal for systemic drug delivery is to provide both spatial and temporal control of drug release. Liposomes have been evaluated as drug delivery vehicles for decades, but their clinical significance has been limited by slow release or poor availability of the encapsulated drug. Here we show that near-complete liposome release can be initiated within seconds by irradiating hollow gold nanoshells (HGNs) with a near-infrared (NIR) pulsed laser. Our findings reveal that different coupling methods such as having the HGNs tethered to, encapsulated within, or suspended freely outside the liposomes, all triggered liposome release but with different levels of efficiency. For the underlying content release mechanism, our experiments suggest that the microbubble formation and collapse due to the rapid temperature increase of the HGN is responsible for liposome disruption, as evidenced by the formation of solid gold particles after the NIR irradiation and the coincidence of a laser power threshold for both triggered release and pressure fluctuations in the solution associated with cavitation. These effects are similar to those induced by ultrasound and our approach is conceptually analogous to the use of optically triggered nano-"sonicators" deep inside the body for drug delivery. We expect HGNs can be coupled with any nanocarriers to promote spatially and temporally controlled drug release. In addition, the capability of external HGNs to permeabilize lipid membranes can facilitate the cellular uptake of macromolecules including proteins and DNA and allow for promising applications in gene therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chapter 14 - Synthesis, characterization, and optical response of gold nanoshells used to trigger release from liposomes.Methods Enzymol. 2009;464:279-307. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)64014-3. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19903560
-
Near Infrared-Triggered Liposome Cages for Rapid, Localized Small Molecule Delivery.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 3;10(1):1706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58764-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32015363 Free PMC article.
-
Liposome-Tethered Gold Nanoparticles Triggered by Pulsed NIR Light for Rapid Liposome Contents Release and Endosome Escape.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 25;14(4):701. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14040701. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35456535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanographene oxide as a switch for CW/pulsed NIR laser triggered drug release from liposomes.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Jan 1;82:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.08.057. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 29025646
-
Light-activatable gold nanoshells for drug delivery applications.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Jun;15(3):741-52. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0097-8. Epub 2014 Feb 19. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014. PMID: 24550102 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmonic Gold Nanostar-Mediated Photothermal Immunotherapy.IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2021 Sep-Oct;27(5):4800109. doi: 10.1109/jstqe.2021.3061462. Epub 2021 Feb 23. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2021. PMID: 34054285 Free PMC article.
-
Shedding light on nanomedicine.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012 Nov-Dec;4(6):638-62. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1188. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22887840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric micelles in anticancer therapy: targeting, imaging and triggered release.Pharm Res. 2010 Dec;27(12):2569-89. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0233-4. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 20725771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Near-Infrared Light Triggered-Release in Deep Brain Regions Using Ultra-photosensitive Nanovesicles.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 May 25;59(22):8608-8615. doi: 10.1002/anie.201915296. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32124529 Free PMC article.
-
General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles.Sci Adv. 2016 Dec 16;2(12):e1601838. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601838. eCollection 2016 Dec. Sci Adv. 2016. PMID: 28028544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sengupta S, Eavarone D, Capila I, Zhao G, Watson N, Kiziltepe T, Sasisekharan R. Nature. 2005;436:568–572. - PubMed
-
- Allen TM, Cullis PR. Science. 2004;303:1818–1822. - PubMed
-
- Ponce AM, Vujaskovic Z, Yuan F, Needham D, Dewhirst MW. International Journal of Hyperthermia. 2006;22:205–213. - PubMed
-
- Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R. Nature Nanotechnology. 2007;2:751–760. - PubMed
-
- Davidsen J, Jorgensen K, Andresen TL, Mouritsen OG. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, Biomembranes. 2003;1609:95–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

