The HIV type 1 epidemic in Bulgaria involves multiple subtypes and is sustained by continuous viral inflow from West and East European countries
- PMID: 18544022
- PMCID: PMC2927039
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2007.0181
The HIV type 1 epidemic in Bulgaria involves multiple subtypes and is sustained by continuous viral inflow from West and East European countries
Abstract
Little is known about the HIV-1 epidemic in Balkan countries. To fill the gap, we investigated the viral genetic diversity in Bulgaria, by sequencing and phylogenetic characterization of 86 plasma samples collected between 2002 and 2006 from seropositive individuals diagnosed within 1986-2006. Analysis of pol gene sequences assigned 51% of the samples to HIV-1 subtype B and 27% to subtype A1. HIV-1 subtype C, F, G, H, and a few putative recombinant forms were also found. Phylogenetic and molecular clock analysis showed a continuous exchange of subtype A and B between Bulgaria and Western as well as other Eastern European countries. At least three separate introductions of HIV-1 subtype A and four of HIV-1 subtype B have occurred within the past 25 years in Bulgaria. The central geographic location of Bulgaria, the substantial genetic heterogeneity of the epidemic with multiple subtypes, and the significant viral flow observed to and from the Balkan countries have the potential to modify the current HIV-1 epidemiological structure in Europe and highlight the importance of more extensive and continuous monitoring of the epidemic in the Balkans.
Figures

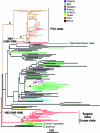
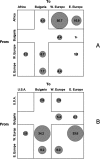
References
-
- EuroHIV (European Centre for the Epidemiological Monitoring of AIDS): HIV/AIDS Surveillance in Europe: Midyear report. 2005.
-
- HIV/AIDS in Europe: Moving from Death Sentence to Chronic Disease Management. In: Matic S, editor; Lazarus JV, editor; Donoghoe MC, editor. WHO Regional Office for Europe; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2006.
-
- Kabakchieva E. Vassileva S. Kelly JA, et al. HIV risk behaviour patterns, predictors, and sexually transmitted disease prevalence in the social networks of young Roma (Gypsy) men in Sofia, Bulgaria. Sex Transm Dis. 2006;33(8):485–490. - PubMed
-
- Kabakchieva E. Amirkhanian YA. Kelly JA. McAuliffe TL. Vassileva S. High levels of sexual HIV/STD risk behaviour among Roma (Gypsy) men in Bulgaria: Pattern and predictors of risk in a representative community sample. Int J STD AIDS. 2002;13(3):184–191. - PubMed
-
- Kelly JA. Amirkhanian YA. Kabakchieva E, et al. Gender roles and HIV sexual risk vulnerability of Roma (Gypsies) men and women in Bulgaria and Hungary: An ethnographic study. AIDS Care. 2004;16(2):231–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

