Superoxide-mediated proteasomal degradation of Bcl-2 determines cell susceptibility to Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 18544562
- PMCID: PMC2516494
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgn137
Superoxide-mediated proteasomal degradation of Bcl-2 determines cell susceptibility to Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis
Abstract
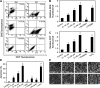
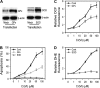
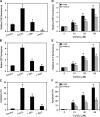
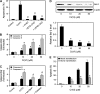
Hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] compounds are redox cycling environmental carcinogens that induce apoptosis as the primary mode of cell death. Defects in apoptosis regulatory mechanisms contribute to carcinogenesis induced by Cr(VI). Activation of apoptosis signaling pathways is tightly linked with the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Likewise, ROS have been implicated in the regulation of Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis and carcinogenicity; however, its role in Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis and the underlying mechanism are largely unknown. We report that ROS, specifically superoxide anion (.O(-)(2), mediates Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis of human lung epithelial H460 cells. H460 rho(0) cells that lack mitochondrial DNA demonstrated a significant decrease in ROS production and apoptotic response to Cr(VI), indicating the involvement of mitochondrial ROS in Cr(VI)-induced apoptosis. In agreement with this observation, we found that Cr(VI) induces apoptosis mainly through the mitochondrial death pathway via caspase-9 activation, which is negatively regulated by the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. Furthermore, .O(-)(2) induced apoptosis in response to Cr(VI) exposure by downregulating and degrading Bcl-2 protein through the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway. This study reveals a novel mechanism linking .O(-)(2) with Bcl-2 stability and provides a new dimension to ROS-mediated Bcl-2 downregulation and apoptosis induction.
Figures

References
-
- Wang S, et al. Role of reactive oxygen species and Cr(VI) in Ras-mediated signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2004;255:119–127. - PubMed
-
- Langard S. One hundred years of chromium and cancer: a review of epidemiological evidence and selected case reports. Am. J. Ind. Med. 1990;17:189–215. - PubMed
-
- Langard S. Role of chemical species and exposure characteristics in cancer among persons occupationally exposed to chromium compounds. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health. 1993;19(suppl. 1):81–89. - PubMed

