TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ regulatory T cells rescue scurfy mice
- PMID: 18546144
- PMCID: PMC2574868
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.200838346
TGF-beta-induced Foxp3+ regulatory T cells rescue scurfy mice
Abstract
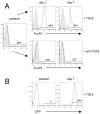
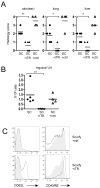
Scurfy mice have a deletion in the forkhead domain of the forkhead transcription factor p3 (Foxp3), fail to develop thymic-derived, naturally occurring Foxp3+ regulatory T cells (nTreg), and develop a fatal lymphoproliferative syndrome with multi-organ inflammation. Transfer of thymic-derived Foxp3+ nTreg into neonatal Scurfy mice prevents the development of disease. Stimulation of conventional CD4+Foxp3(-) via the TCR in the presence of TGF-beta and IL-2 induces the expression of Foxp3 and an anergic/suppressive phenotype. To determine whether the TGF-beta-induced Treg (iTreg) were capable of suppressing disease in the Scurfy mouse, we reconstituted newborn Scurfy mice with polyclonal iTreg. Scurfy mice treated with iTreg do not show any signs of disease and have drastically reduced cell numbers in peripheral lymph nodes and spleen in comparison to untreated Scurfy controls. The iTreg retained their expression of Foxp3 in vivo for 21 days, migrated into the skin, and prevented the development of inflammation in skin, liver and lung. Thus, TGF-beta-differentiated Foxp3+ Treg appear to possess all of the functional properties of thymic-derived nTreg and represent a potent population for the cellular immunotherapy of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Shevach EM. CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:389–400. - PubMed
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Regulatory T cells in the control of immune pathology. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:816–822. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakihama T, Itoh M, Kuniyasu Y, et al. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunol Rev. 2001;182:18–32. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–336. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, Kelly TE, et al. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet. 2001;27:20–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

