Dopamine modulates diurnal and circadian rhythms of protein phosphorylation in photoreceptor cells of mouse retina
- PMID: 18547251
- PMCID: PMC2440701
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06224.x
Dopamine modulates diurnal and circadian rhythms of protein phosphorylation in photoreceptor cells of mouse retina
Abstract
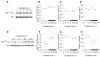
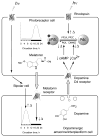
Many aspects of photoreceptor metabolism are regulated as diurnal or circadian rhythms. The nature of the signals that drive rhythms in mouse photoreceptors is unknown. Dopamine amacrine cells in mouse retina express core circadian clock genes, leading us to test the hypothesis that dopamine regulates rhythms of protein phosphorylation in photoreceptor cells. To this end we investigated the phosphorylation of phosducin, an abundant photoreceptor-specific phosphoprotein. In mice exposed to a daily light-dark cycle, robust daily rhythms of phosducin phosphorylation and retinal dopamine metabolism were observed. Phospho-phosducin levels were low during the daytime and high at night, and correlated negatively with levels of the dopamine metabolite 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid. The effect of light on phospho-phosducin levels was mimicked by pharmacological activation of dopamine D4 receptors. The amplitude of the diurnal rhythm of phospho-phosducin was reduced by > 50% in D4 receptor-knockout mice, due to higher daytime levels of phospho-phosducin. In addition, the daytime level of phospho-phosducin was significantly elevated by L-745,870, a dopamine D4 receptor antagonist. These data indicate that dopamine and other light-dependent processes cooperatively regulate the diurnal rhythm of phosducin phosphorylation. Under conditions of constant darkness a circadian rhythm of phosducin phosphorylation was observed, which correlated negatively with the circadian rhythm of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid levels. The circadian fluctuation of phospho-phosducin was completely abolished by constant infusion of L-745,870, indicating that the rhythm of phospho-phosducin level is driven by dopamine. Thus, dopamine release in response to light and circadian clocks drives daily rhythms of protein phosphorylation in photoreceptor cells.
Figures

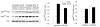
Similar articles
-
Phosducin regulates transmission at the photoreceptor-to-ON-bipolar cell synapse.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 3;30(9):3239-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4775-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20203183 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D₄ receptor activation controls circadian timing of the adenylyl cyclase 1/cyclic AMP signaling system in mouse retina.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Jul;34(1):57-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07734.x. Epub 2011 Jun 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21676039 Free PMC article.
-
Light-driven translocation of the protein phosphatase 2A complex regulates light/dark dephosphorylation of phosducin and rhodopsin.Biochemistry. 2002 Nov 19;41(46):13526-38. doi: 10.1021/bi0204490. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12427013
-
Dopamine D4-like receptors in vertebrate retina: does the retina offer a model for the D4-receptor analysis?Pol J Pharmacol. 1997 Aug;49(4):201-11. Pol J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9437763 Review.
-
Circadian clock organization in the retina: From clock components to rod and cone pathways and visual function.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023 May;94:101119. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2022.101119. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36503722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Retina and Other Light-sensitive Ocular Clocks.J Biol Rhythms. 2016 Jun;31(3):223-43. doi: 10.1177/0748730416642657. Epub 2016 Apr 19. J Biol Rhythms. 2016. PMID: 27095816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopaminergic amacrine cell number, plexus density, and dopamine content in the mouse retina: Strain differences and effects of Bax gene disruption.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Dec;177:208-212. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 30240584 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Light Adaptation of ON-Sustained Ganglion Cells in Early Diabetes Is Attributable to Diminished Response to Dopamine D4 Receptor Activation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Jan 3;63(1):33. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.1.33. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 35077550 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of melatonin receptor 1 in mouse retina and its role in the circadian regulation of the electroretinogram and dopamine levels.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024483. Epub 2011 Sep 7. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21915336 Free PMC article.
-
Pgc-1α and Nr4a1 Are Target Genes of Circadian Melatonin and Dopamine Release in Murine Retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Sep;56(10):6084-94. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-17503. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 26393668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adachi A, Nogi T, Ebihara S. Phase-relationship and mutual effects between circadian rhythms of ocular melatonin and dopamine in the pigeon. Brain Res. 1998;792:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Bartell PA, Miranda-Anaya M, McIvor W, Menaker M. Interactions between dopamine and melatonin organize circadian rhythmicity in the retina of the green iguana. J Biol Rhythms. 2007;22:515–523. - PubMed
-
- Besharse JC, Iuvone PM, Pierce ME. Regulation of rhythmic photoreceptor metabolism: A role for post-receptoral neurons. Progress in Retinal Research. 1988;7:21–61.
-
- Brown BM, Carlson BL, Zhu X, Lolley RN, Craft CM. Light-driven translocation of the protein phosphatase 2A complex regulates light/dark dephosphorylation of phosducin and rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 2002;41:13526–13538. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Lee RH. Phosducin and betagamma-transducin interaction I: effects of post-translational modifications. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;233:370–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

