Association of anemia and erythropoiesis stimulating agents with inflammatory biomarkers in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 18547996
- PMCID: PMC2739585
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2008.245
Association of anemia and erythropoiesis stimulating agents with inflammatory biomarkers in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Inflammatory cytokines are important predictors of cardiovascular mortality especially in patients with chronic kidney disease. Here we explored the relationship of anemia and epoetin treatment to inflammatory cytokine levels in patients with chronic kidney disease. One hundred non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease over 18 years of age were evenly split into anemic and non-anemic cohorts. Of the 50 anemic patients, 23 were receiving erythropoiesis stimulating agents treatments. Levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha were found to be significantly higher and serum albumin was significantly lower with trends towards higher interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in anemic compared to non-anemic patients. Further analysis by multiple logistic regression found that anemic patients treated with erythropoiesis stimulating agents had significantly higher odds for the upper two quartiles for IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha compared to non-anemic patients. Our study found that the anemia of chronic kidney disease was associated with up regulation of TNF-alpha, and possibly IL-6 and IL-8 along with increased levels of these proinflammatory cytokines in patients treated with epoetin.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Singh reports receiving consulting fees from Ortho Biotech Clinical Affairs/Johnson and Johnson, Amgen, Roche, Merck, Abbott, Watson and lecture fees from Ortho Biotech Clinical Affairs/Johnson and Johnson, Roche, Amgen, and Watson; serving on advisory boards for Ortho Biotech Clinical Affairs, Roche, Watson, AMAG, and Amgen; and receiving grant support from Ortho Biotech Clinical Affairs, Roche, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen, Watson. Dr Singh is the Medical Director of Dialysis Clinics Inc. Dr Goligorsky, Dr Patel, Dr Mittal, Dr Addabbo, and Dr Keithi-Reddy report no conflicts of interests.
Figures
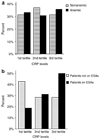
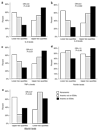
Comment in
-
The mortality risk associated with higher hemoglobin: is the therapy to blame?Kidney Int. 2008 Sep;74(6):695-7. doi: 10.1038/ki.2008.263. Kidney Int. 2008. PMID: 18756292 Review.
References
-
- Jurkovitz CT, Abramson JL, Vaccarino LV, et al. Association of high serum creatinine and anemia increases the risk of coronary events: results from the prospective community-based atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:2919–2925. - PubMed
-
- Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, et al. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2085–2098. - PubMed
-
- Drueke TB, Locatelli F, Clyne N, et al. Normalization of hemoglobin level in patients with chronic kidney disease and anemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2071–2084. - PubMed
-
- Smith KJ, Bleyer AJ, Little WC, et al. The cardiovascular effects of erythropoietin. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;59:538–548. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Cook NR. Biomarkers for prediction of cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1472–1473. author reply 1474–1475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

