The first 5 minutes after greater occipital nerve block
- PMID: 18549410
- PMCID: PMC4029494
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01146.x
The first 5 minutes after greater occipital nerve block
Abstract
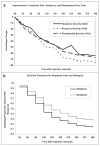
We performed greater occipital nerve blocks on 24 migraineurs with unilateral migraine and trigeminal nerve distribution allodynia. Using a visual analog scale for migraine pain, brush allodynia in the trigeminal nerve distribution and photophobia were reduced 64%, 75%, and 67%, respectively, after 5 minutes. Allodynia improved faster than headache. The results of this study suggest that greater occipital nerve blocks initiate an inhibitory process that shuts down several symptom generators.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Burstein R, Yarnitsky D, Goor-Aryeh I, Ransil BJ, Bajwa ZH. An association between migraine and cutaneous allodynia. Ann Neurol. 2000;47:614–624. - PubMed
-
- Burstein R, Collins B, Jakubowski M. Defeating migraine pain with triptans: A race against the developing allodynia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Young WB. The effects of greater occipital nerve block and trigger point injection on brush allodynia and pain in migraine. Headache. 2005;45:350–354. - PubMed
-
- Afridi SK, Shields KG, Bhola R, Goadsby PJ. Greater occipital nerve injection in primary headache syndromes –Prolonged effects from a single injection. Pain. 2006;122:126–129. - PubMed
-
- Gale GD, Caputi CA, Firetto V. Therapeutic blockade of the greater occipital and supraorbital nerves in migraine patients. Headache. 1998;38:57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

