Potential advantages of cell administration on the inflammatory response compared to standard ACE inhibitor treatment in experimental myocardial infarction
- PMID: 18549470
- PMCID: PMC2435101
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-6-30
Potential advantages of cell administration on the inflammatory response compared to standard ACE inhibitor treatment in experimental myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Bone Marrow (BM) progenitor cells can target the site of myocardial injury, contributing to tissue repair by neovascolarization and/or by a possible direct paracrine effect on the inflammatory cascade. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I) are effective in reducing mortality and preventing left ventricular (LV) function deterioration after myocardial infarction.
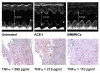
Methods: We investigated the short term effects of BM mononuclear cells (BMMNCs) therapy on the pro-inflammatory cytokines (pro-CKs) and on LV remodelling and compared these effects over a standard ACE-I therapy in a rat model of myocardial cryodamage. Forty two adult inbread Fisher-F344 rats were randomized into three groups: untreated (UT; n = 12), pharmacological therapy (ACE-I; n = 14, receiving quinapril), and cellular therapy (BMMNCs; n = 16, receiving BMMNCs infusion). Rats underwent to a standard echocardiogram in the acute setting and 14 days after the damage, before the sacrifice. Pro-CKs analysis (interleukin (IL)1beta, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)alpha was performed (multiplex proteome arrays) on blood samples obtained by direct aorta puncture before the sacrifice; a control group of 6 rats was considered as reference.
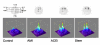
Results: Concerning the extension of the infarcted area as well as the LV dimensions, no differences were observed among the animal groups; treated rats had lower left atrial diameters and higher indexes of LV function. Pro-Cks were increased in infarcted-UT rats if compared with controls, and significantly reduced by BMMNCs and ACE-I ; TNFalpha inversely correlated with LV fractional shortening.
Conclusion: After myocardial infarction, both BMMNCs and ACE-I reduce the pattern of pro-Ck response, probably contributing to prevent the deterioration of LV function observed in UT rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor prevents left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction in angiotensin II type 1 receptor knockout mice.Heart. 2005 Aug;91(8):1080-5. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2004.035618. Heart. 2005. PMID: 16020603 Free PMC article.
-
Late coronary artery reperfusion has additive beneficial effects on infarct expansion when combined with early angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor therapy post myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2001 Jan;15(1):49-54. doi: 10.1023/a:1011110801971. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2001. PMID: 11504163
-
Should increasing the dose or adding an AT1 receptor blocker follow a relatively low dose of ACE inhibitor initiated in acute myocardial infarction?Cardiovasc Res. 2003 Jun 1;58(3):611-20. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00318-3. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12798434
-
Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on ventricular remodeling and survival following myocardial infarction.Ann Pharmacother. 1993 Jun;27(6):755-66. doi: 10.1177/106002809302700617. Ann Pharmacother. 1993. PMID: 8329800 Review.
-
Role of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in preventing left ventricular remodelling following myocardial infarction.Eur Heart J. 1995 Nov;16 Suppl K:42-8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/16.suppl_k.42. Eur Heart J. 1995. PMID: 8869135 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 downregulation of ACE2 and pleiotropic effects of ACEIs/ARBs.Hypertens Res. 2020 Sep;43(9):985-986. doi: 10.1038/s41440-020-0488-z. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Hypertens Res. 2020. PMID: 32523133 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Timing of bone marrow cell delivery has minimal effects on cell viability and cardiac recovery after myocardial infarction.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010 Jan;3(1):77-85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.109.872085. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010. PMID: 19920031 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of mucosal inflammation in uncomplicated diverticular disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Jul;56(7):2098-103. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1547-0. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21221786
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) Downregulation During Coronavirus Infection.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 13. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01277-5. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39266903 Review.
-
The puzzle of sharing bio-molecular targets between coronaviruses and mediators of the cardiovascular system in humans: Looking for plausible hypotheses.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Aug;141:109793. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109793. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32361530 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ciulla MM, Lazzari L, Pacchiana R, Esposito A, Bosari S, Ferrero S, Gianelli U, Paliotti R, Busca G, Giorgetti A, Magrini F, Rebulla P. Homing of peripherally injected bone marrow cells in rat after experimental myocardial injury. Haematologica. 2003;88:614–21. - PubMed
-
- Templin C, Kotlarz D, Marquart F, Faulhaber J, Brendecke V, Schaefer A, Tsikas D, Bonda T, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Ohl L, Naim HY, Foerster R, Drexler H, Limbourg FP. Transcoronary delivery of bone marrow cells to the infracted murine myocardium: feasibility, cellular kinetics, and improvement in cardiac function. Basic Res Cardiol. 2006;101:301–10. doi: 10.1007/s00395-006-0590-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

