Isolation and characterization of side population stem cells in articular synovial tissue
- PMID: 18549504
- PMCID: PMC2440379
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-86
Isolation and characterization of side population stem cells in articular synovial tissue
Abstract
Background: Autologous chondrocyte implantation is an established technique for the repair of degenerated articular cartilage. Recently, the detection of side population (SP) cells, which have the ability to strongly efflux Hoechst 33342 (Ho) fluorescence dye, has attracted attention as a method of stem cell isolation. Although SP cells from synovial tissue were expected to be an excellent source for this tissue engineering, their precise character in the synovial tissue has not been determined.
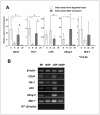
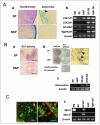
Methods: Synovial tissues from bovine metacarpophalangeal joints were used as a stem cell source. For efficient collection of stem cells, we first prepared a preculture before sorting in medium containing FBS at variable concentrations for 4 days. Using a cell sorter and the Ho-dye, a poorly stained population enriched with stem cells was then isolated. To determine the characteristics of the stem cells, specific marker genes such as CD34, Flk-1, c-Kit, Abcg-2 were identified by real-time PCR. Sorted SP cells were cultured in a stem cell medium supplemented with bFGF, SCF and fibronectin, and evaluated for their differentiation potentials into chondrocytes, osteocytes and myocytes.
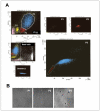
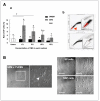
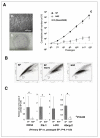
Results: SP cells of synovium tissue were increased from 2% of the total cell population to approximately 10% of the total cells by preculture in the 1%FBS contained medium. Sorted SP cells expressed CD34, Flk-1, c-Kit, Abcg-2 and Mdr-1 -all are important marker genes for stem cell characteristics. The SP cells could be further expanded ex vivo while maintaining stem cell potentials such as marker gene expression, Ho-dye efflux potential and multiple differentiation potentials into chondrocyte, osteocyte and myocyte.
Conclusion: In the present study, we demonstrated that the cells with outstanding stem cell properties were efficiently collected as a SP fraction from bovine synovial membrane. Furthermore, we have described an efficient isolation method and the culture conditions for ex vivo expansion that maintains their important characteristics. Our results suggest that the SP cells of synovium tissue might be important candidates as sources for cell transplantation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of chondrogenesis and superficial zone protein accumulation in synovial side population cells by BMP-7 and TGF-beta1.J Orthop Res. 2008 Apr;26(4):485-92. doi: 10.1002/jor.20521. J Orthop Res. 2008. PMID: 17972329
-
Accelerated and safe proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells in medium supplemented with human serum.J Nippon Med Sch. 2012;79(6):444-52. doi: 10.1272/jnms.79.444. J Nippon Med Sch. 2012. PMID: 23291843
-
BMP-2 induces the expression of chondrocyte-specific genes in bovine synovium-derived progenitor cells cultured in three-dimensional alginate hydrogel.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005 Jun;13(6):527-36. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2005.02.006. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005. PMID: 15922187
-
The Potential for Synovium-derived Stem Cells in Cartilage Repair.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Feb 23;13(3):174-184. doi: 10.2174/1574888X12666171002111026. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 28969580 Review.
-
Formation of synovial joints and articular cartilage.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2013 Aug;72(3):181-7. doi: 10.5603/fm.2013.0031. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2013. PMID: 24068678 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells Derived from Articular Cartilage, Synovial Membrane and Synovial Fluid for Cartilage Regeneration: Current Status and Future Perspectives.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017 Oct;13(5):575-586. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9753-1. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2017. PMID: 28721683 Review.
-
9-phenyl acridine photosensitizes A375 cells to UVA radiation.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 3;6(9):e04733. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04733. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32944667 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical Phenotyping and Modulation of ALDH+ Inflammatory Breast Cancer Stem-Like Cells.Small. 2019 Feb;15(5):e1802891. doi: 10.1002/smll.201802891. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Small. 2019. PMID: 30632269 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac side population cells: moving toward the center stage in cardiac regeneration.Circ Res. 2012 May 11;110(10):1355-63. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243014. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22581921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and characterization of multi-drug resistant, prostate carcinoma-initiating stem-like cells from human prostate cancer cell lines 22RV1.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Jul;340(1-2):265-73. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0426-5. Epub 2010 Mar 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20224986
References
-
- Mochizuki T, Muneta T, Sakaguchi Y, Nimura A, Yokoyama A, Koga H, Sekiya I. Higher chondrogenic potential of fibrous synovium- and adipose synovium-derived cells compared with subcutaneous fat-derived cells: distinguishing properties of mesenchymal stem cells in humans. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:843–853. doi: 10.1002/art.21651. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

