A missense mutation in the sodium phosphate co-transporter Slc34a1 impairs phosphate homeostasis
- PMID: 18550648
- PMCID: PMC2518441
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007121360
A missense mutation in the sodium phosphate co-transporter Slc34a1 impairs phosphate homeostasis
Abstract
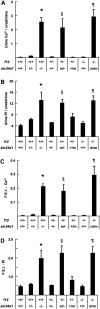
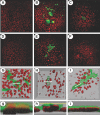
The sodium phosphate co-transporters Npt2a and Npt2c play important roles in the regulation of phosphate homeostasis. Slc34a1, the gene encoding Npt2a, resides downstream of the gene encoding coagulation factor XII (f12) and was inadvertently modified while generating f12(-/-) mice. In this report, the renal consequences of this modification are described. The combined single allelic mutant Slc34a1m contains two point mutations in exon 13: A499V is located in intracellular loop 5, and V528M is located in transmembrane domain 11. In addition to the expected coagulopathy of the f12(-/-) phenotype, mice homozygous for the double allelic modification (f12(-/-)/slc34a1(m/m)) displayed hypophosphatemia, hypercalcemia, elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase, urolithiasis, and hydronephrosis. Strategic cross-breedings demonstrated that the kidney-related pathology was associated only with autosomal recessive transmission of the slc34a1(m) gene and was not influenced by the simultaneous inactivation of f12. Npt2a[V528M] could be properly expressed in opossum kidney cells, but Npt2a[A499V] could not. These results suggest that a single amino acid substitution in Npt2a can lead to improper translocation of the protein to the cell membrane, disturbance of phosphate homeostasis, and renal calcification. Whether point mutations in the SLC34A1 gene can lead to hypophosphatemia and nephrolithiasis in humans remains unknown.
Figures




Comment in
-
Of men and mice: who is in control of renal phosphate reabsorption?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Sep;19(9):1625-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008060611. Epub 2008 Jul 23. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18650475 No abstract available.
References
-
- Forster IC, Kohler K, Biber J, Murer H: Forging the link between structure and function of electrogenic cotransporters: The renal type IIa Na+/Pi cotransporter as a case study. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 80: 69–108, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Murer H, Forster I, Biber J: The sodium phosphate cotransporter family SLC34. Pflugers Arch 447: 763–767, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Forster IC, Hernando N, Biber J, Murer H: Proximal tubular handling of phosphate: A molecular perspective. Kidney Int 70: 1548–1559, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Tenenhouse HS: Phosphate transport: Molecular basis, regulation and pathophysiology. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 103: 572–577, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Shimada T, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki Y, Muto T, Hino R, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T: FGF-23 is a potent regulator of vitamin D metabolism and phosphate homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res 19: 429–435, 2004 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

