CTCF physically links cohesin to chromatin
- PMID: 18550811
- PMCID: PMC2448833
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801273105
CTCF physically links cohesin to chromatin
Abstract
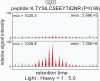
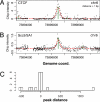
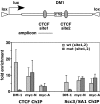
Cohesin is required to prevent premature dissociation of sister chromatids after DNA replication. Although its role in chromatid cohesion is well established, the functional significance of cohesin's association with interphase chromatin is not clear. Using a quantitative proteomics approach, we show that the STAG1 (Scc3/SA1) subunit of cohesin interacts with the CCTC-binding factor CTCF bound to the c-myc insulator element. Both allele-specific binding of CTCF and Scc3/SA1 at the imprinted IGF2/H19 gene locus and our analyses of human DM1 alleles containing base substitutions at CTCF-binding motifs indicate that cohesin recruitment to chromosomal sites depends on the presence of CTCF. A large-scale genomic survey using ChIP-Chip demonstrates that Scc3/SA1 binding strongly correlates with the CTCF-binding site distribution in chromosomal arms. However, some chromosomal sites interact exclusively with CTCF, whereas others interact with Scc3/SA1 only. Furthermore, immunofluorescence microscopy and ChIP-Chip experiments demonstrate that CTCF associates with both centromeres and chromosomal arms during metaphase. These results link cohesin to gene regulatory functions and suggest an essential role for CTCF during sister chromatid cohesion. These results have implications for the functional role of cohesin subunits in the pathogenesis of Cornelia de Lange syndrome and Roberts syndromes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
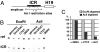
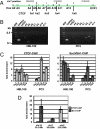
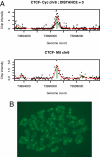
Similar articles
-
Nonallelic transcriptional roles of CTCF and cohesins at imprinted loci.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(15):3094-104. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01449-10. Epub 2011 May 31. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21628529 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase II beta interacts with cohesin and CTCF at topological domain borders.Genome Biol. 2016 Aug 31;17(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1043-8. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27582050 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of genomic neighbourhood at the imprinted IGF2-H19 locus in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and Silver-Russell syndrome.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Apr 1;20(7):1363-74. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr018. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21282187 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide studies of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and cohesin provide insight into chromatin structure and regulation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):30906-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R111.324962. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22952237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CTCF: the protein, the binding partners, the binding sites and their chromatin loops.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 May 6;368(1620):20120369. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0369. Print 2013. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23650640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SA1 binds directly to DNA through its unique AT-hook to promote sister chromatid cohesion at telomeres.J Cell Sci. 2013 Aug 1;126(Pt 15):3493-503. doi: 10.1242/jcs.130872. Epub 2013 May 31. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23729739 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation modulated genetic variant effect on gene transcriptional regulation.Genome Biol. 2023 Dec 8;24(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03130-5. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 38066556 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing throws descriptive 3-D genome folding studies for a loop.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016 Jul;8(4):286-99. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1338. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27265842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cohesinopathies, gene expression, and chromatin organization.J Cell Biol. 2010 Apr 19;189(2):201-10. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912129. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20404106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a new CCCTC-binding factor binding site as a dual regulator of Epstein-Barr virus latent infection.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jan 25;19(1):e1011078. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011078. eCollection 2023 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36696451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osborne CS, et al. Active genes dynamically colocalize to shared sites of ongoing transcription. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1065–1071. - PubMed
-
- Capelson M, Corces VG. Boundary elements and nuclear organization. Biol Cell. 2004;96:617–629. - PubMed
-
- Krueger C, Osborne CS. Raising the curtains on interchromosomal interactions. Trends Genet. 2006;22:637–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

