Notch1 and TGFbeta1 cooperatively regulate Foxp3 expression and the maintenance of peripheral regulatory T cells
- PMID: 18550850
- PMCID: PMC2518888
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-144980
Notch1 and TGFbeta1 cooperatively regulate Foxp3 expression and the maintenance of peripheral regulatory T cells
Abstract
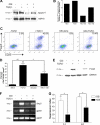
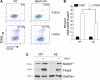
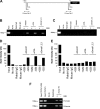
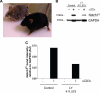
Notch and its ligands have been implicated in the regulation and differentiation of various CD4(+) T-helper cells. Regulatory T cells (T(regs)), which express the transcription factor Foxp3, suppress aberrant immune responses that are typically associated with autoimmunity or excessive inflammation. Previous studies have shown that transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta1) induces Foxp3 expression and a regulatory phenotype in peripheral T cells. Here, we show that pharmacologic inhibition of Notch signaling using gamma-secretase inhibitor (GSI) treatment blocks (1) TGFbeta1-induced Foxp3 expression, (2) the up-regulation of Foxp3-target genes, and (3) the ability to suppress naive T-cell proliferation. In addition, the binding of Notch1, CSL, and Smad to conserved binding sites in the foxp3 promoter can be inhibited by treatment with GSI. Finally, in vivo administration of GSI results in reduced Foxp3 expression and development of symptoms consistent with autoimmune hepatitis, a disease previously found to result from dysregulation of TGFbeta signaling and regulatory T cells. Together, these findings indicate that the Notch and TGFbeta signaling pathways cooperatively regulate Foxp3 expression and regulatory T-cell maintenance both in vitro and in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Osborne BA, Minter LM. Notch signalling during peripheral T-cell activation and differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:64–75. - PubMed
-
- Parks AL, Curtis D. Presenilin diversifies its portfolio. Trends Genet. 2007;23:140–150. - PubMed
-
- Aster JC. Deregulated NOTCH signaling in acute T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: new insights, questions, and opportunities. Int J Hematol. 2005;82:295–301. - PubMed
-
- Siemers ER, Quinn JF, Kaye J, et al. Effects of a gamma-secretase inhibitor in a randomized study of patients with Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2006;66:602–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

