Pivotal role of angiotensin II receptor subtype 1A in the development of two-kidney, one-clip hypertension: study in angiotensin II receptor subtype 1A knockout mice
- PMID: 18551014
- PMCID: PMC2704388
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282fe6eaa
Pivotal role of angiotensin II receptor subtype 1A in the development of two-kidney, one-clip hypertension: study in angiotensin II receptor subtype 1A knockout mice
Abstract
Objective: The present study was performed to examine in two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) Goldblatt hypertensive mice: first, the relative contribution of angiotensin II receptor subtypes 1A (AT(1A)) and 1B (AT(1B)); second, the role of angiotensin II type 2 (AT(2)) receptors in the development of hypertension in wild-type (AT(1A)+/+) and AT(1A) receptor knockout (AT(1A)-/-) mice; and third, the role of increased nitric oxide synthase activity in counteracting the hypertensinogenic action of angiotensin II in this model.
Methods: AT(1A)+/+ and AT(1A)-/- mice underwent clipping of one renal artery and were infused with either saline vehicle or selective AT(2) receptor agonist CGP-42112A (CGP). Blood pressure was monitored by radiotelemetry. Blood pressure responses to the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor nitro-L-arginine-methyl-ester were evaluated.
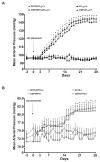
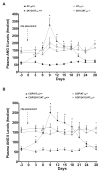
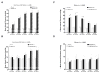
Results: AT(1A)+/+ mice responded to clipping by a rise in blood pressure that was not modified by CGP infusion. Clip placement caused a slight increase in blood pressure in AT(1A)-/- mice that remained significantly lower than in AT(1A)+/+ mice. Acute nitric oxide synthase inhibition caused greater increase in blood pressure in 2K1C/AT(1A)+/+ than in AT(1A)+/+ mice.
Conclusion: The present data support the critical role of AT(1A) receptors in the development of 2K1C hypertension, whereas AT(1B) receptors play only a minor role in blood pressure regulation in this model of angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Activation of AT(2) receptors does not play an antagonistic role in the AT(1) receptor-mediated hypertensinogenic actions of angiotensin II in this model. Finally, enhanced nitric oxide synthase activity plays a protective role by counteracting the vasoconstrictor influences of angiotensin II in 2K1C hypertensive mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Navar LG, Zou L, Von Thun A, Wang CT, Imig JD, Mitchell KD. Unraveling the mystery of Goldblatt hypertension. News Physiol Sci. 1998;13:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Cervenka L, Wang CT, Mitchell KD, Navar LG. Proximal tubular angiotensin II levels and renal functional responses to AT1 receptor blockade in nonclipped kidneys of Goldblatt hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1999;33:102–107. - PubMed
-
- Kobori H, Nangaku M, Navar LG, Nishiyama A. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system: from physiology to the pathobiology of hypertension and kidney disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59:251–287. - PubMed
-
- Ingert C, Grima M, Coquard C, Barthelmers M, Imbs JL. Contribution of angiotensin II internalization to intrarenal angiotensin II levels in rats. Am J Physiol. 2002;283:F1003–F1010. - PubMed
-
- Navar LG, Nishiyama A. Why are angiotensin concentrations so high in the kidney? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004;13:107–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

