Interaction of G-protein beta3 subunit and nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms on carotid artery intima-media thickness in young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study
- PMID: 18551105
- PMCID: PMC4348699
- DOI: 10.1038/ajh.2008.188
Interaction of G-protein beta3 subunit and nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms on carotid artery intima-media thickness in young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study
Abstract
Background: G-protein beta3 subunit (GNB3) gene C825T and endothelial nitric oxide (eNOS) gene G894T polymorphisms both influence arterial structure and function. However, information is scant regarding the interaction of these genes on arterial wall thickness.
Methods: This aspect was examined in 654 white and black subjects, aged 25-43 years (72.9% white, 39.3% male). Arterial wall thickness was assessed in terms of the average intima-media thickness (IMT) of common carotid, internal carotid, and carotid bulb segments by B-mode ultrasonography.
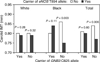
Results: Frequencies of T allele of the GNB3 C825T polymorphism (0.718 vs. 0.304, P < 0.0001) and G allele of the eNOS G894T polymorphism (0.868 vs. 0.661, P < 0.0001) were higher in blacks compared to whites. In a multivariate model including gender, age, mean arterial pressure, body mass index, triglycerides/HDL cholesterol ratio, insulin resistance index, smoking, and/or race, there was no significant genotypic effect on carotid IMT with respect to GNB3 C825T or eNOS G894T polymorphisms among whites, blacks, and total sample. However, the carriers of TT genotype of the GNB3 C825T and T allele of the eNOS G894T had a significantly lower carotid IMT among blacks (P = 0.003) and the total sample (P = 0.006).
Conclusion: These results indicate that the genetic variations of the eNOS gene in combination with the GNB3 gene jointly influence carotid artery wall thickening process in young adults, especially in blacks.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G-6A polymorphism of angiotensinogen gene modulates the effect of blood pressure on carotid intima-media thickness. The Bogalusa Heart Study.Am J Hypertens. 2007 Oct;20(10):1073-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2007.06.001. Am J Hypertens. 2007. PMID: 17903690
-
Nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphism (G894T) influences arterial stiffness in adults: The Bogalusa Heart Study.Am J Hypertens. 2004 Jul;17(7):553-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjhyper.2004.02.021. Am J Hypertens. 2004. PMID: 15233973
-
Q192R polymorphism of the paraoxanase 1 gene and its association with serum lipoprotein variables and carotid artery intima-media thickness in young adults from a biracial community. The Bogalusa Heart Study.Atherosclerosis. 2004 Nov;177(1):167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.06.013. Atherosclerosis. 2004. PMID: 15488880
-
Genetic effects on carotid intima-media thickness: systematic assessment and meta-analyses of candidate gene polymorphisms studied in more than 5000 subjects.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010 Feb;3(1):15-21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.834366. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010. PMID: 20160191
-
Childhood risk factors predict adult risk associated with subclinical cardiovascular disease. The Bogalusa Heart Study.Am J Cardiol. 2002 Nov 21;90(10C):3L-7L. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(02)02953-3. Am J Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12459418 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of the eNOS G894T gene polymorphism with target organ damage in children with newly diagnosed primary hypertension.Pediatr Nephrol. 2015 Dec;30(12):2189-97. doi: 10.1007/s00467-015-3164-9. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 26227630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burke GL, Evans GW, Riley WA, Sharrett AR, Howard G, Barnes RW, Rosamond W, Crow RS, Rautaharju PM, Heiss G. Arterial wall thickness is associated with prevalent cardiovascular disease in middle-aged adults. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Stroke. 1995;26:386–391. - PubMed
-
- Hodis HN, Mack WJ, LaBree L, Selzer RH, Liu CR, Liu CH, Azen SP. The role of carotid arterial intima-media thickness in predicting clinical coronary events. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128:262–269. - PubMed
-
- Heiss G, Sharrett AR, Barnes R, Chambless LE, Szklo M, Alzola C. Carotid atherosclerosis measured by B-mode ultrasound in populations: associations with cardiovascular risk factors in the ARIC study. Am J Epidemiol. 1991;134:250–256. - PubMed
-
- Urbina EM, Srinivasan SR, Tang R, Bond MG, Kieltyka L, Berenson GS Bogalusa Heart Study. Impact of multiple coronary risk factors on the intima-media thickness of different segments of carotid artery in healthy young adults (The Bogalusa Heart Study) Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:953–958. - PubMed
-
- Bhuiyan AR, Srinivasan SR, Chen W, Paul TK, Berenson GS. Correlates of vascular structure and function measures in asymptomatic young adults: the Bogalusa Heart Study. Atherosclerosis. 2006;189:1–7. - PubMed

