Machine-learning approaches for classifying haplogroup from Y chromosome STR data
- PMID: 18551166
- PMCID: PMC2396484
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000093
Machine-learning approaches for classifying haplogroup from Y chromosome STR data
Abstract
Genetic variation on the non-recombining portion of the Y chromosome contains information about the ancestry of male lineages. Because of their low rate of mutation, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the markers of choice for unambiguously classifying Y chromosomes into related sets of lineages known as haplogroups, which tend to show geographic structure in many parts of the world. However, performing the large number of SNP genotyping tests needed to properly infer haplogroup status is expensive and time consuming. A novel alternative for assigning a sampled Y chromosome to a haplogroup is presented here. We show that by applying modern machine-learning algorithms we can infer with high accuracy the proper Y chromosome haplogroup of a sample by scoring a relatively small number of Y-linked short tandem repeats (STRs). Learning is based on a diverse ground-truth data set comprising pairs of SNP test results (haplogroup) and corresponding STR scores. We apply several independent machine-learning methods in tandem to learn formal classification functions. The result is an integrated high-throughput analysis system that automatically classifies large numbers of samples into haplogroups in a cost-effective and accurate manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
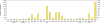
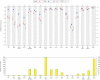

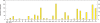
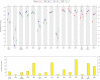
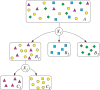

 . Given a sample x = (x
1,…xL), its likelihood under a haplogroup is the product of its evaluated locus bin frequencies.
. Given a sample x = (x
1,…xL), its likelihood under a haplogroup is the product of its evaluated locus bin frequencies.

References
-
- Jobling MA, Pandya A, Tyler-Smith C. The Y chromosome in forensic analysis and paternity testing. Int J Legal Med. 1997;110:118–124. - PubMed
-
- Hammer MF, Chamberlain VF, Kearney VF, Stover D, Zhang G, et al. Population structure of Y chromosome SNP haplogroups in the United States and forensic implications for constructing Y chromosome STR databases. Forensic Sci Int. 2006;164:45–55. - PubMed
-
- Jobling MA, Tyler-Smith C. New uses for new haplotypes - the human Y chromosome, disease and selection. Trends Genet. 2000;16:356–362. - PubMed
-
- Jobling MA. In the name of the father: surnames and genetics. Trends Genet. 2001;17:353–357. - PubMed
-
- Stone AC, Milner GR, Paabo S, Stoneking M. Sex determination of ancient human skeletons using DNA. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1996;99:231–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

