SINE RNA induces severe developmental defects in Arabidopsis thaliana and interacts with HYL1 (DRB1), a key member of the DCL1 complex
- PMID: 18551175
- PMCID: PMC2408557
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000096
SINE RNA induces severe developmental defects in Arabidopsis thaliana and interacts with HYL1 (DRB1), a key member of the DCL1 complex
Abstract
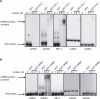
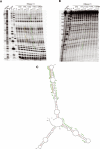
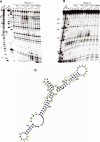
The proper temporal and spatial expression of genes during plant development is governed, in part, by the regulatory activities of various types of small RNAs produced by the different RNAi pathways. Here we report that transgenic Arabidopsis plants constitutively expressing the rapeseed SB1 SINE retroposon exhibit developmental defects resembling those observed in some RNAi mutants. We show that SB1 RNA interacts with HYL1 (DRB1), a double-stranded RNA-binding protein (dsRBP) that associates with the Dicer homologue DCL1 to produce microRNAs. RNase V1 protection assays mapped the binding site of HYL1 to a SB1 region that mimics the hairpin structure of microRNA precursors. We also show that HYL1, upon binding to RNA substrates, induces conformational changes that force single-stranded RNA regions to adopt a structured helix-like conformation. Xenopus laevis ADAR1, but not Arabidopsis DRB4, binds SB1 RNA in the same region as HYL1, suggesting that SINE RNAs bind only a subset of dsRBPs. Consistently, DCL4-DRB4-dependent miRNA accumulation was unchanged in SB1 transgenic Arabidopsis, whereas DCL1-HYL1-dependent miRNA and DCL1-HYL1-DCL4-DRB4-dependent tasiRNA accumulation was decreased. We propose that SINE RNA can modulate the activity of the RNAi pathways in plants and possibly in other eukaryotes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Specific interactions between Dicer-like proteins and HYL1/DRB-family dsRNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2005 Jan;57(2):173-88. doi: 10.1007/s11103-004-6853-5. Plant Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15821876
-
A dominant mutation in DCL1 suppresses the hyl1 mutant phenotype by promoting the processing of miRNA.RNA. 2009 Mar;15(3):450-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.1297109. Epub 2009 Jan 20. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19155326 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between DCL1 and HYL1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis.RNA. 2006 Feb;12(2):206-12. doi: 10.1261/rna.2146906. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16428603 Free PMC article.
-
Plant dicer-like proteins: double-stranded RNA-cleaving enzymes for small RNA biogenesis.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):33-44. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0877-1. Epub 2016 Nov 24. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27885504 Review.
-
HYL1's multiverse: A journey through miRNA biogenesis and beyond canonical and non-canonical functions of HYL1.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024 Aug;80:102546. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102546. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38718678 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical requirements for two Dicer-like activities from wheat germ.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 23;10(1):e0116736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116736. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25615604 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of Plant Virus Protein Encoded by the 5'-Proximal Gene of Tetra-Cistron Movement Block.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 15;24(18):14144. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814144. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762447 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding RNAs in Response to Drought Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 20;22(22):12519. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212519. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA biogenesis, degradation and activity in plants.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jan;72(1):87-99. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1728-7. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25209320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional control of miRNA abundance in Arabidopsis.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Nov;7(11):1443-6. doi: 10.4161/psb.21956. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22960761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kramerov DA, Vassetzky NS. Short retroposons in eukaryotic genomes. Int Rev Cytol. 2005;247:165–221. - PubMed
-
- Arnaud P, Yukawa Y, Lavie L, Pelissier T, Sugiura M, et al. Analysis of the SINE S1 pol III promoter from Brassica; impact of methylation and influence of external sequences. Plant Journal. 2001;26:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Dewannieux M, Esnault C, Heidmann T. LINE-mediated retrotransposition of marked Alu sequences. Nature Genetics. 2003;35:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Ohshima K, Okada N. SINEs and LINEs: symbionts of eukaryotic genomes with a common tail. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2005;110:475–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

