Hypocretin/orexin and nociceptin/orphanin FQ coordinately regulate analgesia in a mouse model of stress-induced analgesia
- PMID: 18551194
- PMCID: PMC2423866
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI35115
Hypocretin/orexin and nociceptin/orphanin FQ coordinately regulate analgesia in a mouse model of stress-induced analgesia
Abstract
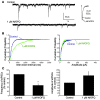
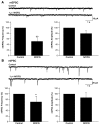
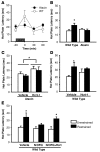
Stress-induced analgesia (SIA) is a key component of the defensive behavioral "fight-or-flight" response. Although the neural substrates of SIA are incompletely understood, previous studies have implicated the hypocretin/orexin (Hcrt) and nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) peptidergic systems in the regulation of SIA. Using immunohistochemistry in brain tissue from wild-type mice, we identified N/OFQ-containing fibers forming synaptic contacts with Hcrt neurons at both the light and electron microscopic levels. Patch clamp recordings in GFP-tagged mouse Hcrt neurons revealed that N/OFQ hyperpolarized, decreased input resistance, and blocked the firing of action potentials in Hcrt neurons. N/OFQ postsynaptic effects were consistent with opening of a G protein-regulated inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channel. N/OFQ also modulated presynaptic release of GABA and glutamate onto Hcrt neurons in mouse hypothalamic slices. Orexin/ataxin-3 mice, in which the Hcrt neurons degenerate, did not exhibit SIA, although analgesia was induced by i.c.v. administration of Hcrt-1. N/OFQ blocked SIA in wild-type mice, while coadministration of Hcrt-1 overcame N/OFQ inhibition of SIA. These results establish what is, to our knowledge, a novel interaction between the N/OFQ and Hcrt systems in which the corticotropin-releasing factor and N/OFQ systems coordinately modulate the Hcrt neurons to regulate SIA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct inhibition of hypocretin/orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus by nociceptin/orphanin FQ blocks stress-induced analgesia in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Mar;60(4):543-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.026. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21195099 Free PMC article.
-
The neuronal circuit between nociceptin/orphanin FQ and hypocretins/orexins coordinately modulates stress-induced analgesia and anxiety-related behavior.Vitam Horm. 2015;97:295-321. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2014.11.004. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Vitam Horm. 2015. PMID: 25677777 Review.
-
Nociceptin/Orphanin-FQ Inhibits Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Neurons via G-Protein-Gated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels.eNeuro. 2018 Dec 26;5(6):ENEURO.0161-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0161-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30627649 Free PMC article.
-
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone increases behavioral arousal through modulation of hypocretin/orexin neurons.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 25;29(12):3705-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0431-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19321767 Free PMC article.
-
Role of innate and drug-induced dysregulation of brain stress and arousal systems in addiction: Focus on corticotropin-releasing factor, nociceptin/orphanin FQ, and orexin/hypocretin.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:145-61. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.027. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20026088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sleep and headache.Semin Neurol. 2009 Sep;29(4):406-18. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1237113. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Semin Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19742415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orquestic regulation of neurotransmitters on reward-seeking behavior.Int Arch Med. 2014 Jun 16;7:29. doi: 10.1186/1755-7682-7-29. eCollection 2014. Int Arch Med. 2014. PMID: 25061480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knock-In Mice with NOP-eGFP Receptors Identify Receptor Cellular and Regional Localization.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 19;35(33):11682-93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5122-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26290245 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic Archaerhodopsin-3 Expression in Hypocretin/Orexin Neurons Engenders Cellular Dysfunction and Features of Type 2 Narcolepsy.J Neurosci. 2019 Nov 20;39(47):9435-9452. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0311-19.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 18. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31628177 Free PMC article.
-
Retrodialysis of N/OFQ into the nucleus accumbens shell blocks cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine and locomotor activity.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Jan 15;699(1-3):200-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.11.050. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23219985 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R43 MH072162/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020811/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH61755/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R44 RR017182/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R44RR017182/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R43MH072162/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020584/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070039/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG020584/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061755/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060711/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DA020811/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS057052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS057052/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK060711/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK070039/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

