Model-based hypothesis testing of key mechanisms in initial phase of insulin signaling
- PMID: 18551197
- PMCID: PMC2424138
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000096
Model-based hypothesis testing of key mechanisms in initial phase of insulin signaling
Abstract
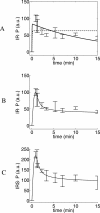
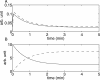
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance of target organs, which is due to impaired insulin signal transduction. The skeleton of signaling mediators that provide for normal insulin action has been established. However, the detailed kinetics, and their mechanistic generation, remain incompletely understood. We measured time-courses in primary human adipocytes for the short-term phosphorylation dynamics of the insulin receptor (IR) and the IR substrate-1 in response to a step increase in insulin concentration. Both proteins exhibited a rapid transient overshoot in tyrosine phosphorylation, reaching maximum within 1 min, followed by an intermediate steady-state level after approximately 10 min. We used model-based hypothesis testing to evaluate three mechanistic explanations for this behavior: (A) phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of IR at the plasma membrane only; (B) the additional possibility for IR endocytosis; (C) the alternative additional possibility of feedback signals to IR from downstream intermediates. We concluded that (A) is not a satisfactory explanation; that (B) may serve as an explanation only if both internalization, dephosphorylation, and subsequent recycling are permitted; and that (C) is acceptable. These mechanistic insights cannot be obtained by mere inspection of the datasets, and they are rejections and thus stronger and more final conclusions than ordinary model predictions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanistic explanations for counter-intuitive phosphorylation dynamics of the insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 in response to insulin in murine adipocytes.FEBS J. 2012 Mar;279(6):987-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08488.x. Epub 2012 Feb 15. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22248283
-
Mass and information feedbacks through receptor endocytosis govern insulin signaling as revealed using a parameter-free modeling framework.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 25;285(26):20171-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.106849. Epub 2010 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20421297 Free PMC article.
-
Altered regulation of insulin signaling components in adipocytes of insulin-resistant type II diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats.Metabolism. 1998 Jan;47(1):54-62. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(98)90193-7. Metabolism. 1998. PMID: 9440478
-
PTP1B and TCPTP--nonredundant phosphatases in insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis.FEBS J. 2013 Jan;280(2):445-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08563.x. Epub 2012 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 22404968 Review.
-
Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance.Exp Mol Med. 2020 Jun;52(6):911-920. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0456-3. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32576931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimal experiment design for model selection in biochemical networks.BMC Syst Biol. 2014 Feb 20;8:20. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-20. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 24555498 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of signaling specificity of insulin and IGF receptors: neglected corners and recent advances.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Feb 28;3:34. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00034. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 22649417 Free PMC article.
-
A hierarchical whole-body modeling approach elucidates the link between in Vitro insulin signaling and in Vivo glucose homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 22;286(29):26028-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188987. Epub 2011 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21572040 Free PMC article.
-
A methodology for global-sensitivity analysis of time-dependent outputs in systems biology modelling.J R Soc Interface. 2012 Sep 7;9(74):2156-66. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0891. Epub 2012 Apr 4. J R Soc Interface. 2012. PMID: 22491976 Free PMC article.
-
In silico generation of alternative hypotheses using causal mapping (CMAP).PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005378. Epub 2009 Apr 29. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19401774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature. 2001;414:799–806. - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson J, Parpal S, Karlsson M, Ramsing C, Thorn H, et al. Localization of the insulin receptor in caveolae of adipocyte plasma membrane. FASEB J. 1999;13:1961–1971. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson M, Thorn H, Danielsson A, Stenkula KG, Öst A, et al. Colocalization of insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate-1 to caveolae in primary human adipocytes. Cholesterol depletion blocks insulin signalling for metabolic and mitogenic control. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:2471–2479. - PubMed
-
- Olefsky JM, Marshall S, Berhanu P, Saekow M, Heidenreich K, et al. Internalization and intracellular processing of insulin and insulin receptors in adipocytes. Metabolism. 1982;31:670–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

