Rare lung disease II: pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- PMID: 18551202
- PMCID: PMC2677953
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/528948
Rare lung disease II: pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
Abstract
The present article is the second in a series on rare lung diseases. It focuses on pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP), a disorder in which lipoproteinaceous material accumulates in the alveolar space. PAP was first described in 1958, and for many years the nature of the material accumulating in the lungs was unknown. Major insights into PAP have been made in the past decade, and these have led to the notion that PAP is an autoimmume disorder in which autoantibodies interfere with signalling through the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor, leading to macrophage and neutrophil dysfunction. This has spurred new therapeutic approaches to this disorder. The discussion of PAP will begin with a case report, then will highlight the classification of PAP and review recent insights into the pathogenesis of PAP. The approach to therapy and the prognosis of PAP will also be discussed.
Le présent article est le deuxième d’une série sur les maladies pulmonaires rares. Il porte sur la protéinose alvéolaire pulmonaire (PAP), un trouble qui provoque l’accumulation de substances lipoprotéinacées dans les espaces alvéolaires. La PAP a été décrite pour la première fois en 1958, et pendant de nombreuses années, la nature de la substance s’accumulant dans les poumons est demeurée inconnue. On a fait d’importantes observations sur la maladie depuis dix ans, lesquelles ont permis d’établir que la PAP est une maladie auto-immune qui provoque l’interférence des auto-anticorps avec la signalisation par le récepteur des facteurs stimulant les colonies de granulocytes-macrophages, provoquant un dysfonctionnement des macrophages et des neutrophiles. Ce constat a suscité de nouvelles démarches thérapeutiques pour cette maladie. L’exposé sur la PAP commence par une étude de cas, puis porte sur la classification de la PAP et l’analyse des récentes observations sur la pathogénèse de la maladie. La démarche à l’égard du traitement et du pronostic de la PAP sera également abordée.
Figures
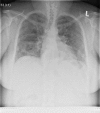
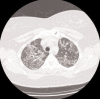
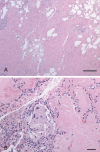
References
-
- Rosen SH, Castleman B, Liebow AA. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 1958;258:1123–42. - PubMed
-
- Seymour JF, Presneill JJ. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: Progress in the first 44 years. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:215–35. - PubMed
-
- Prakash UB, Barham SS, Carpenter HA, Dines DE, Marsh HM. Pulmonary alveolar phospholipoproteinosis: Experience with 34 cases and a review. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987;62:499–518. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein LS, Kavuru MS, Curtis-McCarthy P, Christie HA, Farver C, Stoller JK. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: Clinical features and outcomes. Chest. 1998;114:1357–62. - PubMed
-
- Ziskind M, Jones RN, Weill H. Silicosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976;113:643–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

