Cross-species infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs by a genotype 4 strain of human hepatitis E virus
- PMID: 18551597
- PMCID: PMC3005714
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.21223
Cross-species infection of specific-pathogen-free pigs by a genotype 4 strain of human hepatitis E virus
Abstract
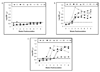
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is an important pathogen. The animal strain of HEV, swine HEV, is related to human HEV. The genotype 3 swine HEV can infect humans and genotype 3 human HEV can infect pigs. The genotype 4 swine and human HEV strains are genetically related, but it is unknown whether genotype 4 human HEV can infect pigs. A swine bioassay was utilized in this study to determine whether genotype 4 human HEV can infect pigs. Fifteen, 4-week-old, specific-pathogen-free pigs were divided into three groups of five each. Group 1 pigs were each inoculated intravenously with PBS buffer as negative controls, group 2 pigs similarly with genotype 3 human HEV (strain US-2), and group 3 pigs similarly with genotype 4 human HEV (strain TW6196E). Serum and fecal samples were collected at 0, 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, and 56 days postinoculation (dpi) and tested for evidence of HEV infection. All pigs were necropsied at 56 dpi. As expected, the negative control pigs remained negative. The positive control pigs inoculated with genotype 3 human HEV all became infected as evidenced by detection of HEV antibodies, viremia and fecal virus shedding. All five pigs in group 3 inoculated with genotype 4 human HEV also became infected: fecal virus shedding and viremia were detected variably from 7 to 56 dpi, and seroconversion occurred by 28 dpi. The data indicated that genotype 4 human HEV has an expanded host range, and the results have important implications for understanding the natural history and zoonosis of HEV.
Figures

References
-
- Arankalle VA, Chobe LP, Chadha MS. Type-IV Indian swine HEV infects rhesus monkeys. Journal of viral hepatitis. 2006;13(11):742–745. - PubMed
-
- Banks M, Heath GS, Grierson SS, King DP, Gresham A, Girones R, Widen F, Harrison TJ. Evidence for the presence of hepatitis E virus in pigs in the United Kingdom. The Veterinary Record. 2004;154(8):223–227. - PubMed
-
- Cooper K, Huang FF, Batista L, Rayo CD, Bezanilla JC, Toth TE, Meng XJ. Identification of genotype 3 hepatitis E virus (HEV) in serum and fecal samples from pigs in Thailand and Mexico, where genotype 1 and 2 HEV strains are prevalent in the respective human populations. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2005;43(4):1684–1688. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drobeniuc J, Favorov MO, Shapiro CN, Bell BP, Mast EE, Dadu A, Culver D, Iarovoi P, Robertson BH, Margolis HS. Hepatitis E virus antibody prevalence among persons who work with swine. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2001;184(12):1594–1597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

