A prototype PET scanner with DOI-encoding detectors
- PMID: 18552140
- PMCID: PMC2662710
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.107.049791
A prototype PET scanner with DOI-encoding detectors
Abstract
Detectors with depth-encoding allow a PET scanner to simultaneously achieve high sensitivity and high spatial resolution.
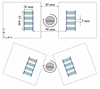
Methods: A prototype PET scanner, consisting of depth-encoding detectors constructed by dual-ended readout of lutetium oxyorthosilicate (LSO) arrays with 2 position-sensitive avalanche photodiodes (PSAPDs), was developed. The scanner comprised 2 detector plates, each with 4 detector modules, and the LSO arrays consisted of 7 x 7 elements, with a crystal size of 0.9225 x 0.9225 x 20 mm and a pitch of 1.0 mm. The active area of the PSAPDs was 8 x 8 mm. The performance of individual detector modules was characterized. A line-source phantom and a hot-rod phantom were imaged on the prototype scanner in 2 different scanner configurations. The images were reconstructed using 20, 10, 5, 2, and 1 depth-of-interaction (DOI) bins to demonstrate the effects of DOI resolution on reconstructed image resolution and visual image quality.
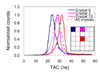
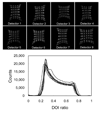
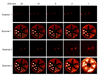
Results: The flood histograms measured from the sum of both PSAPD signals were only weakly depth-dependent, and excellent crystal identification was obtained at all depths. The flood histograms improved as the detector temperature decreased. DOI resolution and energy resolution improved significantly as the temperature decreased from 20 degrees C to 10 degrees C but improved only slightly with a subsequent temperature decrease to 0 degrees C. A full width at half maximum (FWHM) DOI resolution of 2 mm and an FWHM energy resolution of 15% were obtained at a temperature of 10 degrees C. Phantom studies showed that DOI measurements significantly improved the reconstructed image resolution. In the first scanner configuration (parallel detector planes), the image resolution at the center of the field of view was 0.9-mm FWHM with 20 DOI bins and 1.6-mm FWHM with 1 DOI bin. In the second scanner configuration (detector planes at a 40 degrees angle), the image resolution at the center of the field of view was 1.0-mm FWHM with 20 DOI bins and was not measurable when using only 1 bin.
Conclusion: PET scanners based on this detector design offer the prospect of high and uniform spatial resolution (crystal size, approximately 1 mm; DOI resolution, approximately 2 mm), high sensitivity (20-mm-thick detectors), and compact size (DOI encoding permits detectors to be tightly packed around the subject and minimizes number of detectors needed).
Figures



References
-
- Cherry SR, Shao Y, Silverman RW, et al. MicroPET: A high resolution PET scanner for imaging small animals. Ieee Transactions on Nuclear Science. 1997 Jun;44(3):1161–1166.
-
- Lecomte R, deKemp RA, Klein R, et al. LabPETtm: A second-generation APD-based digital scanner for high-resolution small animal PET imaging. Medical Physics. 2006 Jul;33(7):2671–2671.
-
- Missimer J, Madi Z, Honer M, Keller C, Schubiger A, Ametamey SM. Performance evaluation of the 16-module quad-HIDAC small animal PET camera. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2004 May;49(10):2069–2081. - PubMed
-
- Surti S, Karp JS, Perkins AE, et al. Imaging performance of A-PET: A small animal PET camera. Ieee Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2005 Jul;24(7):844–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
