Targeted degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor ICK4/KRP6 by RING-type E3 ligases is essential for mitotic cell cycle progression during Arabidopsis gametogenesis
- PMID: 18552199
- PMCID: PMC2483368
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.059741
Targeted degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor ICK4/KRP6 by RING-type E3 ligases is essential for mitotic cell cycle progression during Arabidopsis gametogenesis
Abstract
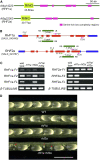
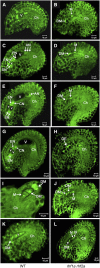
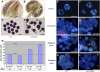
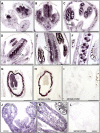
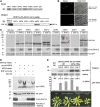
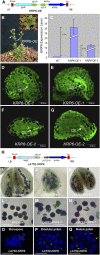
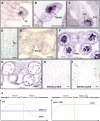
Following meiosis, plant gametophytes develop through two or three rounds of mitosis. Although the ontogeny of gametophyte development has been defined in Arabidopsis thaliana, the molecular mechanisms regulating mitotic cell cycle progression are not well understood. Here, we report that RING-H2 group F 1a (RHF1a) and RHF2a, two RING-finger E3 ligases, play an important role in Arabidopsis gametogenesis. The rhf1a rhf2a double mutants are defective in the formation of male and female gametophytes due to interphase arrest of the mitotic cell cycle at the microspore stage of pollen development and at female gametophyte stage 1 of embryo sac development. We demonstrate that RHF1a directly interacts with and targets a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor ICK4/KRP6 (for Interactors of Cdc2 Kinase 4/Kip-related protein 6) for proteasome-mediated degradation. Inactivation of the two redundant RHF genes leads to the accumulation of ICK4/KRP6, and reduction of ICK4/KRP6 expression largely rescues the gametophytic defects in rhf1a rhf2a double mutants, indicating that ICK4/KRP6 is a substrate of the RHF E3 ligases. Interestingly, in situ hybridization showed that ICK4/KRP6 was predominantly expressed in sporophytes during meiosis. Our findings indicate that RHF1a/2a-mediated degradation of the meiosis-accumulated ICK4/KRP6 is essential to ensure the progression of subsequent mitoses to form gametophytes in Arabidopsis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ubiquitin ligation RINGs twice: redundant control of plant processes by E3 ubiquitin ligases.Plant Cell. 2008 Jun;20(6):1424. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.200611. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18552197 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alexander, M.P. (1969). Differential staining of aborted and nonaborted pollen. Stain Technol. 44 117–122. - PubMed
-
- Butaye, K.M., Goderis, I.J., Wouters, P.F., Pues, J.M., Delaure, S.L., Broekaert, W.F., Depicker, A., Cammue, B.P., and De Bolle, M.F. (2004). Stable high-level transgene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana using gene silencing mutants and matrix attachment regions. Plant J. 39 440–449. - PubMed
-
- Christensen, C.A., Subramanian, S., and Drews, G.N. (1998). Identification of gametophytic mutations affecting female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Dev. Biol. 202 136–151. - PubMed
-
- Daxinger, L., Hunter, B., Sheikh, M., Jauvion, V., Gasciolli, V., Vaucheret, H., Matzke, M., and Furner, I. (2008). Unexpected silencing effects from T-DNA tags in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 13 4–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

