Arabidopsis DDB1-CUL4 ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 forms a nuclear E3 ubiquitin ligase with DDB1 and CUL4 that is involved in multiple plant developmental processes
- PMID: 18552200
- PMCID: PMC2483375
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.058891
Arabidopsis DDB1-CUL4 ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 forms a nuclear E3 ubiquitin ligase with DDB1 and CUL4 that is involved in multiple plant developmental processes
Abstract
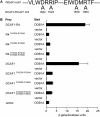
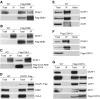
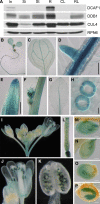
The human DDB1-CUL4 ASSOCIATED FACTOR (DCAF) proteins have been reported to interact directly with UV-DAMAGED DNA BINDING PROTEIN1 (DDB1) through the WDxR motif in their WD40 domain and function as substrate-recognition receptors for CULLIN4-based E3 ubiquitin ligases. Here, we identified and characterized a homolog of human DCAF1/VprBP in Arabidopsis thaliana. Yeast two-hybrid analysis demonstrated the physical interaction between DCAF1 and DDB1 from Arabidopsis, which is likely mediated via the WD40 domain of DCAF1 that contains two WDxR motifs. Moreover, coimmunoprecipitation assays showed that DCAF1 associates with DDB1, RELATED TO UBIQUITIN-modified CUL4, and the COP9 signalosome in vivo but not with CULLIN-ASSOCIATED and NEDDYLATION-DISSOCIATED1, CONSTITUTIVE PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1 (COP1), or the COP10-DET1-DDB1 complex, supporting the existence of a distinct Arabidopsis CUL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase, the CUL4-DDB1-DCAF1 complex. Transient expression of fluorescently tagged DCAF1, DDB1, and CUL4 in onion epidermal cells showed their colocalization in the nucleus, consistent with the notion that the CUL4-DDB1-DCAF1 complex functions as a nuclear E3 ubiquitin ligase. Genetic and phenotypic analysis of two T-DNA insertion mutants of DCAF1 showed that embryonic development of the dcaf1 homozygote is arrested at the globular stage, indicating that DCAF1 is essential for plant embryogenesis. Reducing the levels of DCAF1 leads to diverse developmental defects, implying that DCAF1 might be involved in multiple developmental pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Arabidopsis CULLIN4-damaged DNA binding protein 1 interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA complexes to regulate photomorphogenesis and flowering time.Plant Cell. 2010 Jan;22(1):108-23. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.065490. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20061554 Free PMC article.
-
ABD1 is an Arabidopsis DCAF substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1-based E3 ligases that acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling.Plant Cell. 2014 Feb;26(2):695-711. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.119974. Epub 2014 Feb 21. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 24563203 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Arabidopsis and rice DWD proteins and their roles as substrate receptors for CUL4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases.Plant Cell. 2008 Jan;20(1):152-67. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055418. Epub 2008 Jan 25. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18223036 Free PMC article.
-
WD40 and CUL4-based E3 ligases: lubricating all aspects of life.Trends Plant Sci. 2011 Jan;16(1):38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.09.007. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Trends Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 20965772 Review.
-
The photomorphogenic repressors COP1 and DET1: 20 years later.Trends Plant Sci. 2012 Oct;17(10):584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Trends Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22705257 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of overexpression of Arabidopsis damaged DNA-binding protein 1A on de-etiolated 1.Planta. 2010 Jan;231(2):337-48. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1056-6. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Planta. 2010. PMID: 19921247
-
Whole-genome resequencing of wild and cultivated cannabis reveals the genetic structure and adaptive selection of important traits.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jul 27;22(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03744-0. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35883045 Free PMC article.
-
The Abundant and Unique Transcripts and Alternative Splicing of the Artificially Autododecaploid London Plane (Platanus × acerifolia).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 23;24(19):14486. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914486. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833935 Free PMC article.
-
BPH1, a novel substrate receptor of CRL3, plays a repressive role in ABA signal transduction.Plant Mol Biol. 2018 Apr;96(6):593-606. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0717-x. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Plant Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29560577
-
Pathological and diagnostic implications of DCAF16 expression in human carcinomas including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and urothelial carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Aug 1;10(8):8585-8591. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Angers, S., Li, T., Yi, X., MacCoss, M.J., Moon, R.T., and Zheng, N. (2006). Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature 443 590–593. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt, A., Lechner, E., Hano, P., Schade, V., Dieterle, M., Anders, M., Dubin, M.J., Benvenuto, G., Bowler, C., Genschik, P., and Hellmann, H. (2006). CUL4 associates with DDB1 and DET1 and its downregulation affects diverse aspects of development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 47 591–603. - PubMed
-
- Byrne, M.E., Groover, A.T., Fontana, J.R., and Martienssen, R.A. (2003). Phyllotactic pattern and stem cell fate are determined by the Arabidopsis homeobox gene BELLRINGER. Development 130 3941–3950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

