Differential cell fates induced by all-trans retinoic acid-treated HL-60 human leukemia cells
- PMID: 18552205
- PMCID: PMC2516907
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1207817
Differential cell fates induced by all-trans retinoic acid-treated HL-60 human leukemia cells
Abstract
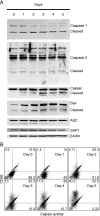
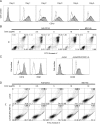
HL-60 human leukemia cells, differentiated into a neutrophil lineage by all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) treatment, express three members of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family, CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1; CD66a), CEACAM3 (CD66d), and CEACAM6 (CD66c). CD66d is a neutrophil lineage-specific marker, and CD66a and CD66c are found on epithelial and other cells. HL-60 cells continuously treated with ATRA underwent apoptosis, and cells transiently treated for 1 day underwent cell-cycle arrest, entered into senescence, and exhibited reduced apoptosis with CD66-positive cells accounting for the majority of live cells. CD66 antigens were also induced in NB4 leukemic cells upon continuous treatment with ATRA. NB4 cells underwent apoptosis with a higher frequency in transient versus continuous-treated cells (38% vs. 19% at Day 5), in contrast to HL-60 cells that underwent cell-cycle arrest and senescence when transiently treated with ATRA. CD66 antigens were not induced in transient, ATRA-treated NB4 cells compared with HL-60 cells. Cell-cycle arrest in HL-60 cells involved reduction in expression levels of p21, cyclins D and E, while Rb1 exhibited reduction in protein levels without changes in mRNA levels over the time course of ATRA treatment. Analysis of several proapoptotic proteins implicated the activation of calpain and cleavage of Bax in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, similar to published studies about the apoptosis of neutrophils. CD1d expression was also induced by ATRA in HL-60 cells and ligation with anti-CD1d antibody-induced apoptosis. In contrast, CD1d-positive primary monocytes were protected from spontaneous apoptosis by CD1d ligation. These studies demonstrate distinct cell fates for ATRA-treated HL-60 cells that provide new insights into ATRA-induced cell differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Mehta K. Retinoids as regulators of gene transcription. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2003;17:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Puccetti E, Ruthardt M. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: PML/RARα and the leukemic stem cell. Leukemia. 2004;18:1169–1175. - PubMed
-
- Tallman M S, Nabhan C, Feusner J H, Rowe J M. Acute promyelocytic leukemia: evolving therapeutic strategies. Blood. 2002;99:759–767. - PubMed
-
- Roninson I B, Dokmanovic M. Induction of senescence-associated growth inhibitors in the tumor-suppressive function of retinoids. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Wright W E, Shay J W. Cellular senescence as a tumor-protection mechanism: the essential role of counting. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:98–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

