Interactions between CB(1) receptors and TRPV1 channels mediated by 12-HPETE are cytotoxic to mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 18552868
- PMCID: PMC2538702
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.246
Interactions between CB(1) receptors and TRPV1 channels mediated by 12-HPETE are cytotoxic to mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons
Abstract
Background and purposes: We recently proposed the existence of neurotoxic interactions between the cannabinoid type 1 (CB(1)) receptor and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels in rat mesencephalic cultures. This study seeks evidence for the mediator(s) and mechanisms underlying the neurotoxic interactions between CB(1) receptors and TRPV1 in vitro and in vivo.
Experimental approach: The mediator(s) and mechanism(s) for the interactions between CB(1) receptors and TRPV1 were evaluated by cell viability assays, immunocytochemistry, Fura-2 calcium imaging, mitochondrial morphology assay, ELISA and Western blot assay in vitro in neuron-enriched mesencephalic cultures. Injections into the substantia nigra and subsequent cell counts were also used to confirm these interactions in vivo.
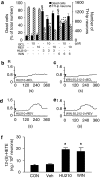
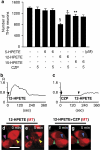
Key results: The neurotoxic interactions were mediated by 12(S)-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HPETE), an endogenous TRPV1 agonist. CB(1) receptor agonists (HU210 and WIN55,212-2) increased the level of 12(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HETE), a downstream metabolite of 12(S)-HPETE, which stimulates TRPV1-mediated death of mesencephalic neurons, both in vitro and in vivo. The neurotoxicity was mediated by increased intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) through TRPV1, consequently leading to mitochondrial damage and was attenuated by baicalein, a 12-lipoxygenase inhibitor.
Conclusion and implications: Activation of CB(1) receptors in rat mesencephalic neurons was associated with biosynthesis of 12(S)-HPETE, which in turn stimulated TRPV1 activity, leading to increased [Ca(2+)](i), mitochondrial damage and neuronal death.
Figures
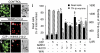
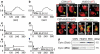

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of renin release by arachidonic acid metabolites, 12(s)-HPETE and 12-HETE: role of TRPV1 channels.Endocrinology. 2011 Oct;152(10):3811-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0141. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21846804 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 mediates cell death of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons in vivo and in vitro.J Neurosci. 2005 Jan 19;25(3):662-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4166-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15659603 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 mediates microglial cell death in vivo and in vitro via Ca2+-mediated mitochondrial damage and cytochrome c release.J Immunol. 2006 Oct 1;177(7):4322-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4322. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16982866
-
Cannabinoid type 1 receptors and transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 channels in fear and anxiety-two sides of one coin?Neuroscience. 2012 Mar 1;204:186-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.08.046. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 21906661 Review.
-
The contribution of TRPV1 channel to 20-HETE-Aggravated ischemic neuronal injury.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018 Jul;137:63-68. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018. PMID: 30041768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Corneal Nerve Fiber Structure, Its Role in Corneal Function, and Its Changes in Corneal Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3242649. doi: 10.1155/2017/3242649. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 29238714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capsaicin in the periaqueductal gray induces analgesia via metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated endocannabinoid retrograde disinhibition.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 May;163(2):330-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01214.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21232043 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of renin release by arachidonic acid metabolites, 12(s)-HPETE and 12-HETE: role of TRPV1 channels.Endocrinology. 2011 Oct;152(10):3811-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-0141. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21846804 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 Hyperfunction Involved in Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate-Mediated Renal Tubular Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6212. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176212. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867359 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation by the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) induces differential responses in corneal epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2010 Sep;91(3):462-71. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.06.022. Epub 2010 Jul 7. Exp Eye Res. 2010. PMID: 20619260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell VA. Tetrahydrocannabinol-induced apoptosis of cultured cortical neurones is associated with cytochrome c release and caspase-3 activation. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:702–709. - PubMed
-
- Canals S, Casarejos MJ, de Bernardo S, Rodriguez-Martin E, Mena MA. Nitric oxide triggers the toxicity due to glutathione depletion in midbrain cultures through 12-lipoxygenase. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:21542–21549. - PubMed
-
- Cannizzaro C, D'Amic OM, Preziosi P, Martire M. Presynaptic effects of anandamide and WIN55,212-2 on glutamatergic nerve endings isolated from rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int. 2006;48:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Carrasco E, Casper D, Werner P. Dopaminergic neurotoxicity by 6-OHDA and MPP+: differential requirement for neuronal cyclooxygenase activity. J Neurosci Res. 2005;81:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Caterina MJ, Julius D. The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:487–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

