Time course profiling of the retinal transcriptome after optic nerve transection and optic nerve crush
- PMID: 18552980
- PMCID: PMC2426719
Time course profiling of the retinal transcriptome after optic nerve transection and optic nerve crush
Abstract
Purpose: A time-course analysis of gene regulation in the adult rat retina after intraorbital nerve crush (IONC) and intraorbital nerve transection (IONT).
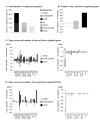
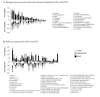
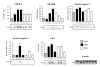
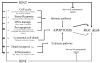
Methods: RNA was extracted from adult rat retinas undergoing either IONT or IONC at increasing times post-lesion. Affymetrix RAE230.2 arrays were hybridized and analyzed. Statistically regulated genes were annotated and functionally clustered. Arrays were validated by means of quantative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) on ten regulated genes at two times post-lesion. Western blotting and immunohistofluorescence for four pro-apoptotic proteins were performed on naïve and injured retinas. Finally, custom signaling maps for IONT- and IONC-induced death response were generated (MetaCore, Genego Inc.).
Results: Here we show that over time, 3,219 sequences were regulated after IONT and 1,996 after IONC. Out of the total of regulated sequences, 1,078 were commonly regulated by both injuries. Interestingly, while IONT mainly triggers a gene upregulation-sustained over time, IONC causes a transitory downregulation. Functional clustering identified the regulation of high interest biologic processes, most importantly cell death wherein apoptosis was the most significant cluster. Ten death-related genes upregulated by both injuries were used for array validation by means of qRT-PCR. In addition, western blotting and immunohistofluorescence of total and active Caspase 3 (Casp3), tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1 associated death domain (TRADD), tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1a (TNFR1a), and c-fos were performed to confirm their protein regulation and expression pattern in naïve and injured retinas. These analyses demonstrated that for these genes, protein regulation followed transcriptional regulation and that these pro-apoptotic proteins were expressed by retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). MetaCore-based death-signaling maps show that several apoptotic cascades were regulated in the retina following optic nerve injury and highlight the similarities and differences between IONT and IONC in cell death profiling.
Conclusions: This comprehensive time course retinal transcriptome study comparing IONT and IONC lesions provides a unique valuable tool to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying optic nerve injury and to design neuroprotective protocols.
Figures

References
-
- Kermer P, Klocker N, Weishaupt JH, Bahr M. Transection of the optic nerve in rats: studying neuronal death and survival in vivo. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2001;7:255–60. - PubMed
-
- Parrilla-Reverter G. Sobrado, P., Mayor, S., Canovas, I., Aguilera, M.E., Lambrou, G.N., Latour. E., Villegas-Pérez, M.P., Vidal-Sanz, M (2004) Intraorbital optic nerve crush induces progressive retinal ganglion cell loss ARVO Annual Meeting; 2004 April 25–29; Fort Lauderdale (FL).
-
- Parrilla-Reverter G. Sobrado, P., Mayor, S., Canovas, I., Bernal, J.M. Soro, M.I., Aguilera, M.E. Villegas-Pérez, M.P., Vidal-Sanz, M (2006) Retinal ganglion cell axotzomy induced by intraorbital nerve crush or optic nerve transection results in different time course degeneration and expression of neurofilaments ARVO Annual Meeting; 2006 April 30-May 4; Fort Lauderdale (FL).
-
- Villegas-Perez MP, Vidal-Sanz M, Rasminsky M, Bray GM, Aguayo AJ. Rapid and protracted phases of retinal ganglion cell loss follow axotomy in the optic nerve of adult rats. J Neurobiol. 1993;24:23–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
