Proteomic surveillance of retinal autoantigens in endogenous uveitis: implication of esterase D and brain-type creatine kinase as novel autoantigens
- PMID: 18552983
- PMCID: PMC2426731
Proteomic surveillance of retinal autoantigens in endogenous uveitis: implication of esterase D and brain-type creatine kinase as novel autoantigens
Abstract
Purpose: Various retinal proteins are newly exposed to immune system in a process of tissue destructive endogenous uveitis. Some of such proteins could be autoantigens that extend the ocular inflammation in human endogenous uveitis. In this study, we aimed to investigate the possibility of such spreading of autoantigens in endogenous uveoretinitis using a proteomic approach.
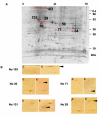
Methods: Experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) was induced in mice by inoculation with a peptide consisting of amino acids 1-20 (GPTHLFQPSLVLDMAKVLLP) of interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein (IRBP). Six weeks after immunization, the presence of autoantibodies against the retinal proteins in mice with EAU were examined by two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by western blotting (2D-WB). Retinal proteins targeted by the autoantibodies were identified by mass spectrometry (MS) and their autoantigenicity in patients with endogenous uveitis, such as Behcet's disease (BD, n=36), Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease (VKH, n=16), and sarcoidosis (n=17) were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results: Six new candidate autoantigens, which were detected in mice with EAU using 2D-WD were identified by MS as beta-actin, esterase D (EsteD), tubulin beta-2, brain-type creatine kinase (BB-CK), voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein, and aspartate aminotransferase. Among the patients with endogenous uveitis, 25% of BD and 25% of VKH patients were positive for anti-EsteD antibody, and 25% of VKH and 38.4% of sarcoidosis patients were positive for anti-BB-CK antibody.
Conclusions: Autoantibodies to EsteD and BB-CK produced in EAU-induced mice were also detected in some endogenous uveitis patients, suggesting that these proteins might be autoantigens spreading in a process of endogenous uveoretinitis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proteomic surveillance of autoimmunity in Behcet's disease with uveitis: selenium binding protein is a novel autoantigen in Behcet's disease.Exp Eye Res. 2007 May;84(5):823-31. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Jan 20. Exp Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17343851
-
Interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein is a potent tolerogen in Lewis rat: suppression of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis is retinal antigen specific.Br J Ophthalmol. 1997 Jan;81(1):61-7. doi: 10.1136/bjo.81.1.61. Br J Ophthalmol. 1997. PMID: 9135411 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for selective accumulation of V beta 8+ T lymphocytes in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induced with two different retinal antigens.J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1627-36. J Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8393049
-
[Intraocular inflammation and homeostasis of the eye].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Mar;113(3):344-77; discussion 378. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19348183 Review. Japanese.
-
[Translational research with experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU)].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007 Mar;111(3):137-58; discussion 159. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17402560 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Vitreous Humor Proteomic Profile in Patients With Vitreoretinal Lymphoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Dec 1;64(15):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.15.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 38038618 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an Autoantibody Against ErbB-3-Binding Protein-1 in the Sera of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:640335. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640335. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34113340 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of DR3 expression in CD4⁺ T cells promotes secretion of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune uveitis.Mol Vis. 2011;17:3486-93. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 22219644 Free PMC article.
-
Isoaspartyl protein damage and repair in mouse retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Mar 13;55(3):1572-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13668. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24550364 Free PMC article.
-
Isoaspartyl formation in creatine kinase B is associated with loss of enzymatic activity; implications for the linkage of isoaspartate accumulation and neurological dysfunction in the PIMT knockout mouse.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 23;9(6):e100622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100622. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24955845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamaki K, Gocho K, Sakuragi S. Pathogenesis of Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 2002;42:13–23. - PubMed
-
- de Smet MD, Bitar G, Mainigi S, Nussenblatt RB. Human S-antigen determinant recognition in uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:3233–8. - PubMed
-
- de Smet MD, Ramadan A. Circulating antibodies to inducible heat shock protein 70 in patients with uveitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2001;9:85–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
