A randomized controlled trial of a novel mixed monoamine reuptake inhibitor in adults with ADHD
- PMID: 18554401
- PMCID: PMC2442604
- DOI: 10.1186/1744-9081-4-24
A randomized controlled trial of a novel mixed monoamine reuptake inhibitor in adults with ADHD
Abstract
Background: NS2359 is a potent reuptake blocker of noradrenalin, dopamine, and serotonin. The aim of the study was to investigate the efficacy, safety and cognitive function of NS2359 in adults with a DSM IV diagnosis of ADHD.
Methods: The study was a multi-centre, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled, parallel group design in outpatient adults (18-55 years) testing 0.5 mg NS2359 vs. placebo for 8 weeks. Multiple assessments including computerized neuropsychological evaluation were performed.
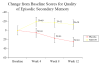
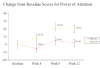
Results: There was no significant difference between NS2359 (n = 63) versus placebo (n = 63) on the primary outcome measure reduction in investigator rated ADHD-RS total score (7.8 versus 6.4; p < 0.45). However, in subjects with the inattentive subtype, there were significantly more responders in the NS2359 group compared to placebo (41% versus 7%; p < 0.01). For all secondary variables (ADHD-RS patient rated; The Conners Adult ADHD Scale; The Brown Adult Scale, and CGI-improvement scale) there were no significant differences between the two groups; however, in the inattentive subgroup, the response to treatment was significantly larger than to placebo. NS2359 improved composite factor scores of attention, episodic- and working memory. No serious adverse events were reported with insomnia, headaches and loss of appetite most commonly reported as side effects.
Conclusion: No overall effect of NS2359 was found on overall symptoms of ADHD. There was also a modest signal of improvement in the inattentive adults with ADHD and cognition warranting further exploration using differing doses.
Figures
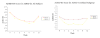
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of mixed amphetamine salts extended release (Adderall XR) in the management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adolescent patients: a 4-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study.Clin Ther. 2006 Feb;28(2):266-79. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2006.02.011. Clin Ther. 2006. PMID: 16678648 Clinical Trial.
-
A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Assessing the Efficacy and Safety of Viloxazine Extended-Release Capsules in Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.CNS Drugs. 2022 Aug;36(8):897-915. doi: 10.1007/s40263-022-00938-w. Epub 2022 Jul 27. CNS Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35896943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dasotraline in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Six-Week, Placebo-Controlled, Fixed-Dose Trial.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019 Mar;29(2):80-89. doi: 10.1089/cap.2018.0083. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30694697 Clinical Trial.
-
Immediate-release methylphenidate for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jan 18;1(1):CD013011. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013011.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33460048 Free PMC article.
-
[Atomoxetine: a new treatment for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents].Encephale. 2005 May-Jun;31(3):337-48. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82399-1. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 16142049 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and tolerability of pharmacotherapies for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults.CNS Drugs. 2011 Sep 1;25(9):737-63. doi: 10.2165/11593070-000000000-00000. CNS Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21870887 Review.
-
Does the difference between physically active and couch potato lie in the dopamine system?Int J Biol Sci. 2010 Mar 9;6(2):133-50. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.6.133. Int J Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20224735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for new drugs to treat binge-eating disorder: Insights from psychopathology and neuropharmacology.J Psychopharmacol. 2022 Jun;36(6):680-703. doi: 10.1177/02698811211032475. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34318734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on the pharmacotherapy of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in adults.Expert Rev Neurother. 2011 Oct;11(10):1443-65. doi: 10.1586/ern.11.137. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011. PMID: 21955201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple reuptake inhibitors as potential next-generation antidepressants: a new hope?Future Med Chem. 2015;7(17):2385-406. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.134. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26619226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilens TE, Prince JB, Biederman J, Spencer TJ, Frances RJ. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and comorbid substance use disorders in adults. Psychiatric Services. 1995;46:761–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

