Diverse aberrancies target yeast mRNAs to cytoplasmic mRNA surveillance pathways
- PMID: 18554525
- PMCID: PMC2614683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.05.006
Diverse aberrancies target yeast mRNAs to cytoplasmic mRNA surveillance pathways
Abstract
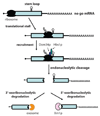
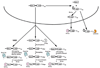
Eukaryotic gene expression is a complex, multistep process that needs to be executed with high fidelity and two general methods help achieve the overall accuracy of this process. Maximizing accuracy in each step in gene expression increases the fraction of correct mRNAs made. Fidelity is further improved by mRNA surveillance mechanisms that degrade incorrect or aberrant mRNAs that are made when a step is not perfectly executed. Here, we review how cytoplasmic mRNA surveillance mechanisms selectively recognize and degrade a surprisingly wide variety of aberrant mRNAs that are exported from the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
Figures


References
-
- Wyers F, Rougemaille M, Badis G, Rousselle JC, Dufour ME, Boulay J, Regnault B, Devaux F, Namane A, Seraphin B, Libri D, Jacquier A. Cryptic pol II transcripts are degraded by a nuclear quality control pathway involving a new poly(A) polymerase. Cell. 2005;121:725–737. - PubMed
-
- Frischmeyer PA, van Hoof A, O'Donnell K, Guerrerio AL, Parker R, Dietz HC. An mRNA surveillance mechanism that eliminates transcripts lacking termination codons. Science. 2002;295:2258–2261. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan CD, Laprade L, Winston F. Transcription elongation factors repress transcription initiation from cryptic sites. Science. 2003;301:1096–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

