Endocytosis of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein together with virus receptor ACE2
- PMID: 18554741
- PMCID: PMC7114441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2008.03.004
Endocytosis of the receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV spike protein together with virus receptor ACE2
Abstract
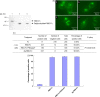
Cell entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is mediated by the viral spike (S) protein. Amino acids 319-510 on the S protein have been mapped as the receptor-binding domain (RBD), which mediates binding to the SARS-CoV receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on SARS-CoV susceptible cells. In this study, we expressed a fusion protein containing the human codon-optimized RBD of the SARS-CoV spike protein linked to the Fc portion of human IgG1 (named RBD-Fc) in HEK293 cells. The RBD-Fc protein was purified by affinity chromatography. The flow cytometry assay showed that the purified RBD-Fc protein could bind to ACE2. We demonstrated that the RBD spike protein alone could be internalized into SARS-CoV susceptible cells together with ACE2. We also showed that the removal of N-glycans from the RBD spike protein did not abolish this phenomenon. Our discoveries may have some implications for the development of the SARS vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single amino acid substitution (R441A) in the receptor-binding domain of SARS coronavirus spike protein disrupts the antigenic structure and binding activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 May 26;344(1):106-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.139. Epub 2006 Mar 30. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16615996 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein contains multiple conformation-dependent epitopes that induce highly potent neutralizing antibodies.J Immunol. 2005 Apr 15;174(8):4908-15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.8.4908. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15814718
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) from raccoon dog can serve as an efficient receptor for the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Gen Virol. 2009 Nov;90(Pt 11):2695-2703. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.013490-0. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19625462
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a functional receptor for SARS coronavirus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Nov;61(21):2738-43. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4242-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15549175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry as a target of antiviral therapies.Antivir Ther. 2007;12(4 Pt B):639-50. Antivir Ther. 2007. PMID: 17944271 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral Respiratory Pathogens and Lung Injury.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 Mar 31;34(3):e00103-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00103-20. Print 2021 Jun 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33789928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in research on ACE2 as a receptor for 2019-nCoV.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(2):531-544. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03611-x. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32780149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Delta SARS-CoV-2 Infection on Glucose Metabolism: Insights on Host Metabolism and Virus Crosstalk in a Feline Model.Viruses. 2024 Feb 15;16(2):295. doi: 10.3390/v16020295. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400070 Free PMC article.
-
Lower Gene Expression of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Receptor in Lung Tissues of Smokers with COVID-19 Pneumonia.Biomolecules. 2021 May 26;11(6):796. doi: 10.3390/biom11060796. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34073591 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA: Vaccine or Gene Therapy? The Safety Regulatory Issues.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10514. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310514. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aruffo A., Stamenkovic I., Melnick M., Underhill C.B., Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990;61:1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Drosten C., Günther S., Preiser W., van der Werf S., Brodt H., Becker S., Rabenau H., Panning M., Kolesnikova L., Fouchier R.A.M., Berger A., Burguière A., Cinatl J., Eickmann M., Escriou N., Grywna K., Kramme S., Manuguerra J., Müller S., Rickerts V., Stürmer M., Vieth S., Klenk H., Osterhaus A.D.M.E., Schmitz H., Doerr H.W. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1967–1976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

