Role of the proteasome in modulating native G-CSFR expression
- PMID: 18554923
- PMCID: PMC2556513
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.04.015
Role of the proteasome in modulating native G-CSFR expression
Abstract
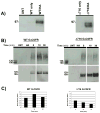
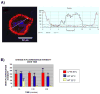
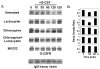
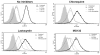
The granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSFR) is a critical regulator of granulopoiesis, but the mechanisms controlling its surface expression are poorly understood. Recent studies using transfected cell lines have suggested the activated G-CSFR is routed to the lysosome and not the proteasome. Here, we examined the role of the ubiquitin/proteasome system in regulating G-CSFR surface expression in both ts20 cells that have a temperature-sensitive E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme and in primary human neutrophils. We show that the G-CSFR is constitutively ubiquitinated, which increases following ligand binding. In the absence of a functional E1 enzyme, ligand-induced internalization of the receptor is inhibited. Pre-treatment of ts20 transfectants with either chloroquine or MG132 inhibited ligand-induced G-CSFR degradation, suggesting a role for both lysosomes and proteasomes in regulating G-CSFR surface expression in this cell line. In neutrophils, inhibition of the proteasome but not the lysosome was found to inhibit internalization/degradation of the activated G-CSFR. Collectively, these data demonstrate the requirement for a functional ubiquitin/proteasome system in G-CSFR internalization and degradation. Our results suggest a prominent role for the proteasome in physiologic modulation of the G-CSFR, and provide further evidence for the importance of the ubiquitin/proteasome system in the initiation of negative signaling by cytokine receptors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
G-CSFR ubiquitination critically regulates myeloid cell survival and proliferation.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003422. Epub 2008 Oct 16. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18923646 Free PMC article.
-
E6AP inhibits G-CSFR turnover and functions by promoting its ubiquitin-dependent proteasome degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Oct;1864(10):1545-1553. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2017.05.026. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28578910
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase Fbw7 negatively regulates granulocytic differentiation by targeting G-CSFR for degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1833(12):2639-2652. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23820376
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling: implications for G-CSF responses and leukemic progression in severe congenital neutropenia.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013 Feb;27(1):61-73, viii. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 23351988 Review.
-
The granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor and its role in disorders of granulopoiesis.Leuk Lymphoma. 1998 Jan;28(3-4):265-73. doi: 10.3109/10428199809092682. Leuk Lymphoma. 1998. PMID: 9517498 Review.
Cited by
-
G-CSF does not influence C2C12 myogenesis despite receptor expression in healthy and dystrophic skeletal muscle.Front Physiol. 2014 May 1;5:170. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00170. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24822049 Free PMC article.
-
Adjusting the balance between effective loading and vector migration of macrophage vehicles to deliver nanoparticles.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 8;8(10):e76024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076024. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116086 Free PMC article.
-
G-CSFR ubiquitination critically regulates myeloid cell survival and proliferation.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003422. Epub 2008 Oct 16. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18923646 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil GM-CSF receptor dynamics in acute lung injury.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Jun;105(6):1183-1194. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MA0918-347R. Epub 2019 Apr 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30942918 Free PMC article.
-
A review of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling and regulation with implications for cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 11;12:932608. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.932608. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Demetri GD, Griffin JD. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood. 1991;78:2791–2808. - PubMed
-
- Williams GJ, Smith CA, Spooncer E, Dexter TM, Taylor DR. Haematopoietic colony stimulating factors promote cell survival by supporting apoptosis. Nature. 1990;343:76–79. - PubMed
-
- Begley CG, Metcalf D, Nicola NA. Binding characteristics and proliferative action of purified granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) on normal and leukemic human promyelocytes. Exp Hematol. 1998;16:71–79. - PubMed
-
- Avalos BR, Gasson JC, Hedvat C, et al. Human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: Biologic activities and receptor characterization on hematopoietic cells and small lung cancer cell lines. Blood. 1990;75:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Hammond WP, Chatta GS, Andrews RG, Dale DC. Abnormal responsiveness of granulocyte committed progenitor cells in cyclic neutropenia. Blood. 1992;79:2536–2539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

