Bioinformatics assessment of beta-myosin mutations reveals myosin's high sensitivity to mutations
- PMID: 18555187
- PMCID: PMC2587080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2008.04.001
Bioinformatics assessment of beta-myosin mutations reveals myosin's high sensitivity to mutations
Erratum in
- Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2010 May;20(4):141
Abstract
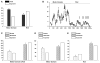
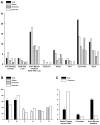
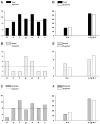
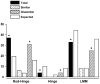
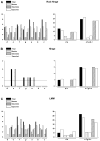
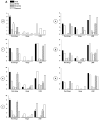
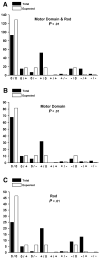
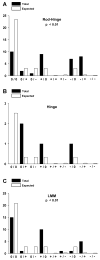
More than 200 mutations in the beta-myosin gene (MYH7) that cause clinically distinct cardiac and/or skeletal myopathies have been reported, but to date, no comprehensive statistical analysis of these mutations has been performed. As a part of this review, we developed a new interactive database and research tool called MyoMAPR (Myopathic Mutation Analysis Profiler and Repository). We report that the distribution of mutations along the beta-myosin gene is not homogeneous, and that myosin is a highly constrained molecule with an uncommon sensitivity to amino acid substitutions. Increasing knowledge of the characteristics of MH7 mutations may provide a valuable resource for scientists and clinicians studying diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment of disease associated with these mutations.
Figures



References
-
- Arad M, Penas-Lado M, Monserrat L, et al. Gene mutations in apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2005;112:2805–2811. - PubMed
-
- Blair E, Redwood C, de Jesus Oliveira M, et al. Mutations of the light meromyosin domain of the beta-myosin heavy chain rod in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2002;90:263–269. - PubMed
-
- Bohlega S, Abu-Amero SN, Wakil SM, et al. Mutation of the slow myosin heavy chain rod domain underlies hyaline body myopathy. Neurology. 2004;62:1518–1521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

